Information and communication technologies (ICTs) and ... - ITU
Information and communication technologies (ICTs) and ... - ITU
Information and communication technologies (ICTs) and ... - ITU
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
appropriate <strong>technologies</strong> <strong>and</strong> approaches are adopted, responding to the needs <strong>and</strong> priorities of each<br />
context.<br />
– Active international engagement: The experience of Ghana also suggests the importance of an active<br />
involvement in international policy processes (e.g., international climate change negotiations, ICT <strong>and</strong><br />
climate change conferences <strong>and</strong> events). These processes contribute to raising high-level political<br />
awareness on <strong>ICTs</strong> <strong>and</strong> climate change adaptation issues, <strong>and</strong> can act as key drivers of policy action <strong>and</strong><br />
innovation in this field.<br />
– Complement policy with research <strong>and</strong> practice: Effective ICT <strong>and</strong> climate change structures should<br />
combine policy action with research <strong>and</strong> practice (e.g. case studies, pilot projects), in order to foster<br />
the development of evidence-based data <strong>and</strong> lessons learned that can inform decision-making, as well<br />
as to identify good practices that can be used in the design of novel e-adaptation approaches <strong>and</strong><br />
initiatives.<br />
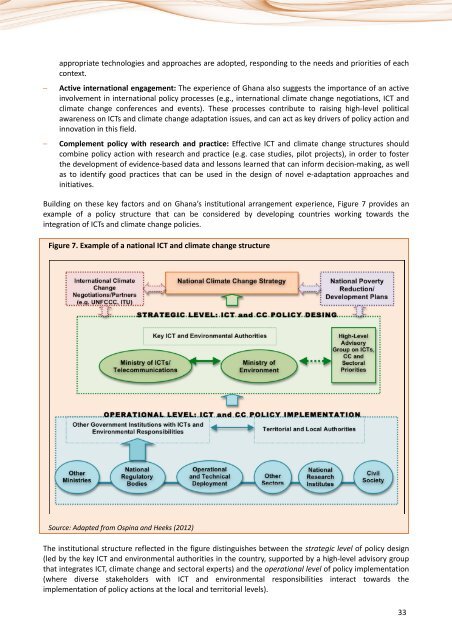
Building on these key factors <strong>and</strong> on Ghana’s institutional arrangement experience, Figure 7 provides an<br />
example of a policy structure that can be considered by developing countries working towards the<br />
integration of <strong>ICTs</strong> <strong>and</strong> climate change policies.<br />
Figure 7. Example of a national ICT <strong>and</strong> climate change structure<br />
Source: Adapted from Ospina <strong>and</strong> Heeks (2012)<br />
The institutional structure reflected in the figure distinguishes between the strategic level of policy design<br />
(led by the key ICT <strong>and</strong> environmental authorities in the country, supported by a high-level advisory group<br />
that integrates ICT, climate change <strong>and</strong> sectoral experts) <strong>and</strong> the operational level of policy implementation<br />
(where diverse stakeholders with ICT <strong>and</strong> environmental responsibilities interact towards the<br />
implementation of policy actions at the local <strong>and</strong> territorial levels).<br />
33