(Jamaica) Limited - FirstCaribbean International Bank
(Jamaica) Limited - FirstCaribbean International Bank
(Jamaica) Limited - FirstCaribbean International Bank
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
notes to the Financial Statements<br />
Year Ended 31 October 2009<br />
(Expressed in <strong>Jamaica</strong>n dollars unless otherwise indicated)<br />
5. Derivative Financial Instruments<br />
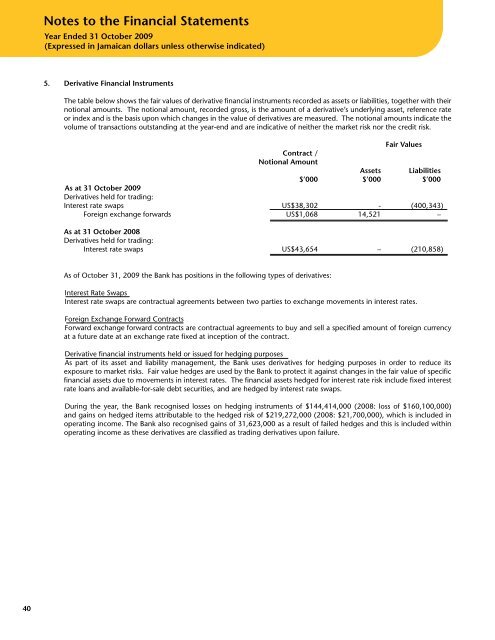
The table below shows the fair values of derivative financial instruments recorded as assets or liabilities, together with their<br />
notional amounts. The notional amount, recorded gross, is the amount of a derivative’s underlying asset, reference rate<br />
or index and is the basis upon which changes in the value of derivatives are measured. The notional amounts indicate the<br />
volume of transactions outstanding at the year-end and are indicative of neither the market risk nor the credit risk.<br />
Fair Values<br />
Contract /<br />
notional Amount<br />
Assets Liabilities<br />
$’000 $’000 $’000<br />
As at 31 October 2009<br />
Derivatives held for trading:<br />
Interest rate swaps US$38,302 - (400,343)<br />
Foreign exchange forwards US$1,068 14,521 –<br />
As at 31 October 2008<br />
Derivatives held for trading:<br />
Interest rate swaps US$43,654 – (210,858)<br />
As of October 31, 2009 the <strong>Bank</strong> has positions in the following types of derivatives:<br />
Interest Rate Swaps<br />
Interest rate swaps are contractual agreements between two parties to exchange movements in interest rates.<br />
Foreign Exchange Forward Contracts<br />
Forward exchange forward contracts are contractual agreements to buy and sell a specified amount of foreign currency<br />
at a future date at an exchange rate fixed at inception of the contract.<br />
Derivative financial instruments held or issued for hedging purposes<br />
As part of its asset and liability management, the <strong>Bank</strong> uses derivatives for hedging purposes in order to reduce its<br />
exposure to market risks. Fair value hedges are used by the <strong>Bank</strong> to protect it against changes in the fair value of specific<br />
financial assets due to movements in interest rates. The financial assets hedged for interest rate risk include fixed interest<br />
rate loans and available-for-sale debt securities, and are hedged by interest rate swaps.<br />
During the year, the <strong>Bank</strong> recognised losses on hedging instruments of $144,414,000 (2008: loss of $160,100,000)<br />
and gains on hedged items attributable to the hedged risk of $219,272,000 (2008: $21,700,000), which is included in<br />
operating income. The <strong>Bank</strong> also recognised gains of 31,623,000 as a result of failed hedges and this is included within<br />
operating income as these derivatives are classified as trading derivatives upon failure.<br />
40