Technical Manual on Utilization of Sympodial Bamboos - ITTO
Technical Manual on Utilization of Sympodial Bamboos - ITTO
Technical Manual on Utilization of Sympodial Bamboos - ITTO
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Chapter 1 The Fundamental Properties <strong>of</strong> Bamboo Timber 5<br />
1 . 3 Chemical Compositi<strong>on</strong> <strong>of</strong><br />
Bamboo Timber<br />
The organic compositi<strong>on</strong> <strong>of</strong> bamboo timber is<br />
quite similar to that <strong>of</strong> wood. It c<strong>on</strong>sists <strong>of</strong> cellulose<br />
(about 55 % ) , lignin (about 25 %) and<br />
hemicellulose (pentosan, about 20% ) .<br />
1.3.1 Hemicellulose<br />
It is mostly composed <strong>of</strong> peritosan, with little<br />
hexoan. 90% <strong>of</strong> hemicellulose in bamboo timber<br />
is made up <strong>of</strong> xylan. Experiments have<br />
shown that bamboo xylan is D-glucuranate arabinoxylan,<br />
which comprises 4-oxygen-methyl<br />
D-glucuranate, L-arabinose and D-xylose.<br />
Their molecule ratio is 1.0: 1.0 -1.3: 24 - 25,<br />
as follows:<br />
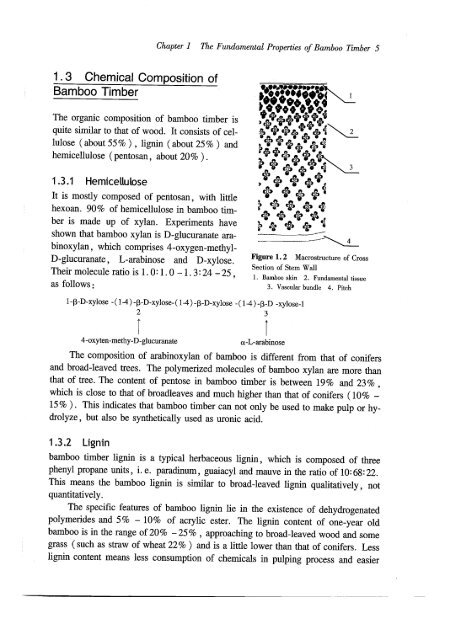
Figure 1. 2 Macrostructure <strong>of</strong> Cross<br />
Secti<strong>on</strong> <strong>of</strong> Stem Wall<br />
1. Bamboo skin 2. Fundamental tissue<br />
3. Vascular bundle 4. Pitch<br />
I-j3-D-xylose -(1-4) -j3-D-xylose-(1-4 ) -j3-D-xylose -(1-4) -j3-D -xylose-l<br />
2 3<br />
r<br />
4-oxyten-methy-D-glucuranate<br />
r<br />
a-L-arabinose<br />
The compositi<strong>on</strong> <strong>of</strong> arabinoxylan <strong>of</strong> bamboo is different from that <strong>of</strong> c<strong>on</strong>ifers<br />
and broad-leaved trees. The polymerized molecules <strong>of</strong> bamboo xylan are more than<br />
that <strong>of</strong> tree. The c<strong>on</strong>tent <strong>of</strong> pentose in bamboo timber is between 19% and 23% ,<br />
which is close to that <strong>of</strong> broadleaves and much higher than that <strong>of</strong> c<strong>on</strong>ifers (10 % -<br />
15% ). This indicates that bamboo timber can not <strong>on</strong>ly be used to make pulp or hydrolyze,<br />
but also be synthetically used as ur<strong>on</strong>ic acid.<br />
1.3.2 Lignin<br />
bamboo timber lignin is a typical herbaceous lignin, which is composed <strong>of</strong> three<br />
phenyl propane units, i. e. paradinum, guaiacyl and mauve in the ratio <strong>of</strong> 10:68:22.<br />
This means the bamboo lignin is similar to broad-leaved lignin qualitatively, not<br />
quantitatively.<br />
The specific features <strong>of</strong> bamboo lignin lie in the existence <strong>of</strong> dehydrogenated<br />
polymerides and 5% - 10% <strong>of</strong> acrylic ester. The lignin c<strong>on</strong>tent <strong>of</strong> <strong>on</strong>e-year old<br />
bamboo is in the range <strong>of</strong>20% -25% , approaching to broad-leaved wood and some<br />
grass (such as straw <strong>of</strong> wheat 22 % ) and is a little lower than that <strong>of</strong> c<strong>on</strong>ifers. Less<br />
lignin c<strong>on</strong>tent means less c<strong>on</strong>sumpti<strong>on</strong> <strong>of</strong> chemicals in pulping process and easier












![[ID]Peta Jalan Menuju Pengelolaan Ramin - ITTO](https://img.yumpu.com/49466232/1/184x260/idpeta-jalan-menuju-pengelolaan-ramin-itto.jpg?quality=85)

![[ID]Review and Measures to Improve Its Implementation - ITTO](https://img.yumpu.com/49270549/1/184x260/idreview-and-measures-to-improve-its-implementation-itto.jpg?quality=85)

