GNS Science Consultancy Report 2006/0XX
GNS Science Consultancy Report 2006/0XX
GNS Science Consultancy Report 2006/0XX
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
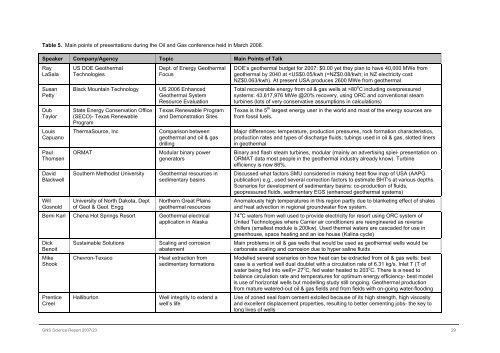
Table 5. Main points of presentations during the Oil and Gas conference held in March <strong>2006</strong>.<br />
Speaker Company/Agency Topic Main Points of Talk<br />
Ray<br />
LaSala<br />
Susan<br />
Petty<br />
Dub<br />
Taylor<br />
Louis<br />
Capuano<br />
Paul<br />
Thomsen<br />
David<br />
Blackwell<br />
Will<br />
Gosnold<br />
US DOE Geothermal<br />
Technologies<br />
Black Mountain Technology<br />
State Energy Conservation Office<br />
(SECO)- Texas Renewable<br />
Program<br />
ThermaSource, Inc<br />
ORMAT<br />
Southern Methodist University<br />
University of North Dakota, Dept<br />
of Geol & Geol. Engg<br />
Dept. of Energy Geothermal<br />
Focus<br />
US <strong>2006</strong> Enhanced<br />
Geothermal System<br />
Resource Evaluation<br />
Texas Renewable Program<br />
and Demonstration Sites<br />
Comparison between<br />
geothermal and oil & gas<br />
drilling<br />
Modular binary power<br />
generators<br />
Geothermal resources in<br />
sedimentary basins<br />
Northern Great Plains<br />
geothermal resources<br />
Berni Karl Chena Hot Springs Resort Geothermal electrical<br />
application in Alaska<br />
Dick<br />
Benoit<br />
Mike<br />
Shook<br />
Prentice<br />
Creel<br />
Sustainable Solutions<br />
Chevron-Texaco<br />
Halliburton<br />
Scaling and corrosion<br />
abatement<br />
Heat extraction from<br />
sedimentary formations<br />
Well integrity to extend a<br />
well’s life<br />
DOE’s geothermal budget for 2007: $0.00 yet they plan to have 40,000 MWe from<br />
geothermal by 2040 at 80 o C including overpressured<br />
systems: 43,617,976 MWe @20% recovery, using ORC and conventional steam<br />
turbines (lots of very conservative assumptions in calculations)<br />
Texas is the 5 th largest energy user in the world and most of the energy sources are<br />
from fossil fuels.<br />
Major differences: temperature, production pressures, rock formation characteristics,<br />
production rates and types of discharge fluids; tubings used in oil & gas, slotted liners<br />
in geothermal<br />
Binary and flash steam turbines, modular (mainly an advertising spiel- presentation on<br />
ORMAT data most people in the geothermal industry already know). Turbine<br />
efficiency is now 88%.<br />
Discussed what factors SMU considered in making heat flow map of USA (AAPG<br />
publication) e.g., used several correction factors to estimate BHT’s at various depths.<br />
Scenarios for development of sedimentary basins: co-production of fluids,<br />
geopressured fluids, sedimentary EGS (enhanced geothermal systems)<br />
Anomalously high temperatures in this region partly due to blanketing effect of shales<br />
and heat advection in regional groundwater flow system.<br />
74 o C waters from well used to provide electricity for resort using ORC system of<br />
United Technologies where Carrier air conditioners are reengineered as reverse<br />
chillers (smallest module is 200kw). Used thermal waters are cascaded for use in<br />
greenhouse, space heating and an ice house (Kalina cycle)<br />
Main problems in oil & gas wells that would be used as geothermal wells would be<br />
carbonate scaling and corrosion due to hyper saline fluids<br />
Modelled several scenarios on how heat can be extracted from oil & gas wells: best<br />
case is a vertical well dual doublet with a circulation rate of 6.31 kg/s. Inlet T (T of<br />
water being fed into well)= 27 o C, fed water heated to 203 o C. There is a need to<br />
balance circulation rate and temperatures for optimum energy efficiency- best model<br />
is use of horizontal wells but modelling study still ongoing. Geothermal production<br />
from mature watered-out oil & gas fields and from fields with on-going water-flooding<br />
Use of zoned seal foam cement extolled because of its high strength, high viscosity<br />
and excellent displacement properties, resulting to better cementing jobs- the key to<br />
long lives of wells<br />
<strong>GNS</strong> <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Report</strong> 2007/23 29