AIS300 - Scheme of Work - Scholarly Commons Home
AIS300 - Scheme of Work - Scholarly Commons Home
AIS300 - Scheme of Work - Scholarly Commons Home
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
communicating using the 802.11 standards (Gast, 2002). The access point (AP) in the<br />
other hand is a device that can function as a relay between nodes that are attached to it.<br />
Access Points can also function as a network bridge that connects WLANs to the wired<br />
LANs. The logical component <strong>of</strong> the WLANs includes the basic service set or also<br />
known as the BSS. As the logical components <strong>of</strong> the WLANs architecture, the basic<br />
service sets (BSS) will provide the management function to a group <strong>of</strong> wireless nodes<br />
(Housley & Arbaugh, 2003; Laet & Schauwers, 2005).<br />
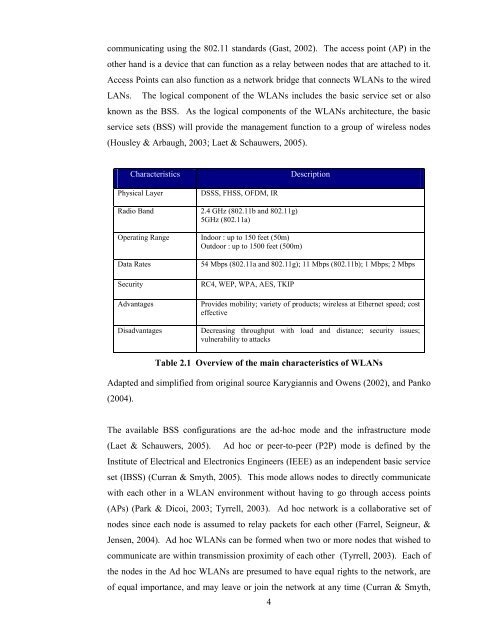
Characteristics<br />
Physical Layer DSSS, FHSS, OFDM, IR<br />
Radio Band 2.4 GHz (802.11b and 802.11g)<br />
5GHz (802.11a)<br />
Operating Range Indoor : up to 150 feet (50m)<br />
Outdoor : up to 1500 feet (500m)<br />
4<br />
Description<br />
Data Rates 54 Mbps (802.11a and 802.11g); 11 Mbps (802.11b); 1 Mbps; 2 Mbps<br />
Security RC4, WEP, WPA, AES, TKIP<br />
Advantages Provides mobility; variety <strong>of</strong> products; wireless at Ethernet speed; cost<br />
effective<br />
Disadvantages Decreasing throughput with load and distance; security issues;<br />
vulnerability to attacks<br />
Table 2.1 Overview <strong>of</strong> the main characteristics <strong>of</strong> WLANs<br />
Adapted and simplified from original source Karygiannis and Owens (2002), and Panko<br />
(2004).<br />
The available BSS configurations are the ad-hoc mode and the infrastructure mode<br />
(Laet & Schauwers, 2005). Ad hoc or peer-to-peer (P2P) mode is defined by the<br />
Institute <strong>of</strong> Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) as an independent basic service<br />
set (IBSS) (Curran & Smyth, 2005). This mode allows nodes to directly communicate<br />
with each other in a WLAN environment without having to go through access points<br />
(APs) (Park & Dicoi, 2003; Tyrrell, 2003). Ad hoc network is a collaborative set <strong>of</strong><br />
nodes since each node is assumed to relay packets for each other (Farrel, Seigneur, &<br />
Jensen, 2004). Ad hoc WLANs can be formed when two or more nodes that wished to<br />
communicate are within transmission proximity <strong>of</strong> each other (Tyrrell, 2003). Each <strong>of</strong><br />
the nodes in the Ad hoc WLANs are presumed to have equal rights to the network, are<br />
<strong>of</strong> equal importance, and may leave or join the network at any time (Curran & Smyth,