Introduction to differential forms
Introduction to differential forms
Introduction to differential forms
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
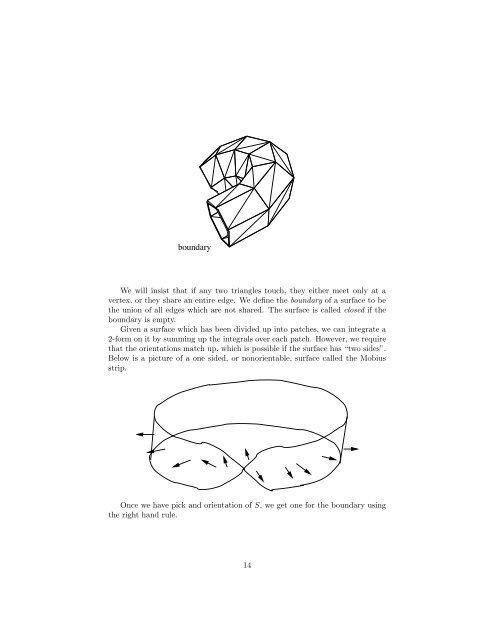
oundary<br />
We will insist that if any two triangles <strong>to</strong>uch, they either meet only at a<br />
vertex, or they share an entire edge. We define the boundary of a surface <strong>to</strong> be<br />
the union of all edges which are not shared. The surface is called closed if the<br />
boundary is empty.<br />
Given a surface which has been divided up in<strong>to</strong> patches, we can integrate a<br />
2-form on it by summing up the integrals over each patch. However, we require<br />
that the orientations match up, which is possible if the surface has “two sides”.<br />
Below is a picture of a one sided, or nonorientable, surface called the Mobius<br />
strip.<br />
Once we have pick and orientation of S, we get one for the boundary using<br />
the right hand rule.<br />
14