Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
C18-AR<br />
(C18 with Phenyl group)<br />
Mechanisms of<br />
Separation<br />
π-π interactions<br />
Dipole-dipole interactions<br />
Hydrophobic binding<br />
interactions<br />
Shape selectivity<br />
Target Analytes<br />
Analytes with π bonding<br />
Analytes with electron delocalization <strong>and</strong> electronwithdrawing<br />
groups, such as halogens, nitro groups,<br />
ketones, esters, <strong>and</strong> acids<br />
Analytes with different dipole moments<br />
Analytes differing in hydrophobicity<br />
Polar, moderately polar, <strong>and</strong> non-polar analytes<br />
Uncharged acids <strong>and</strong> bases<br />
Strength of<br />
Interaction<br />
Strong<br />
Moderate<br />
Strong<br />
Moderate<br />
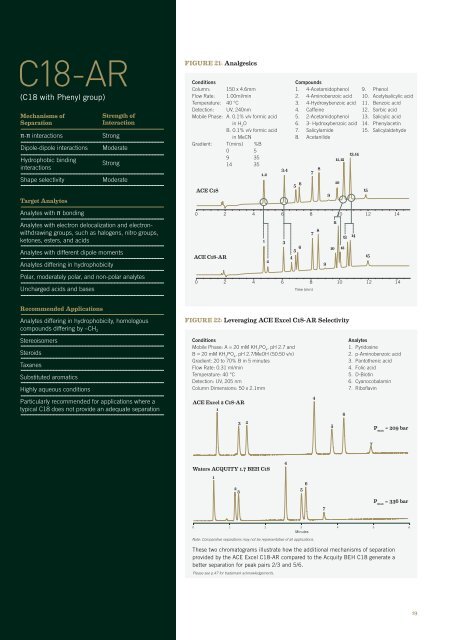
FIGURE 21: Analgesics<br />
Conditions<br />
Column: 150 x 4.6mm<br />
Flow Rate: 1.00ml/min<br />
Temperature: 40 °C<br />
Detection: UV, 240nm<br />
Mobile Phase: A. 0.1% v/v formic acid<br />
in H 2<br />
O<br />
B. 0.1% v/v formic acid<br />
in MeCN<br />
Gradient: T(mins) %B<br />
0 5<br />
9 35<br />
14 35<br />
3,4<br />
1,2<br />
ACE C18<br />
ACE C18-AR<br />
Compounds<br />
1. 4-Acetamidophenol<br />
2. 4-Aminobenzoic acid<br />
3. 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid<br />
4. Caffeine<br />
5. 2-Acetamidophenol<br />
6. 3- Hydroxybenzoic acid<br />
7. Salicylamide<br />
8. Acetanilide<br />
5 6 7 8 9<br />
9. Phenol<br />
10. Acetylsalicylic acid<br />
11. Benzoic acid<br />
12. Sorbic acid<br />
13. Salicylic acid<br />
14. Phenylacetin<br />
15. Salicylaldehyde<br />
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14<br />
11<br />
1<br />
2<br />
3<br />
7 8<br />
5 6<br />
4<br />
9<br />
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14<br />
Time (min)<br />
10<br />
11,12<br />
10<br />
13,14<br />
15<br />
13 14<br />
12<br />
15<br />
Recommended Applications<br />
Analytes differing in hydrophobicity, homologous<br />
compounds differing by –CH 2<br />
Stereoisomers<br />
Steroids<br />
Taxanes<br />
Substituted aromatics<br />
Highly aqueous conditions<br />
Particularly recommended for applications where a<br />
typical C18 does not provide an adequate separation<br />
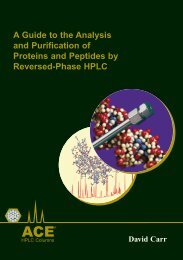
Figure 22: Leveraging ACE Excel C18-AR Selectivity<br />
Conditions<br />
Mobile Phase: A = 20 mM KH 2<br />
PO 4<br />
, pH 2.7 <strong>and</strong><br />
B = 20 mM KH 2<br />
PO 4<br />
, pH 2.7/MeOH (50:50 v/v)<br />
Gradient: 20 to 70% B in 5 minutes<br />
Flow Rate: 0.31 ml/min<br />
Temperature: 40 °C<br />
Detection: UV, 205 nm<br />
Column Dimensions: 50 x 2.1mm<br />
ACE Excel 2 C18-AR<br />
1<br />
3 2<br />
4<br />
5<br />
6<br />
Analytes<br />
1. Pyridoxine<br />
2. p-Aminobenzoic acid<br />
3. Pantothenic acid<br />
4. Folic acid<br />
5. D-Biotin<br />
6. Cyanocobalamin<br />
7. Riboflavin<br />
P max<br />
= 209 bar<br />
7<br />
4<br />
Waters ACQUITY 1.7 BEH C18<br />
1<br />
6<br />
2 3<br />
5<br />
7<br />
P max<br />
= 336 bar<br />
0 1 2 3 4 5 6<br />
Minutes<br />
Note: Comparative separations may not be representative of all applications.<br />
These two chromatograms illustrate how the additional mechanisms of separation<br />
provided by the ACE Excel C18-AR compared to the Acquity BEH C18 generate a<br />
better separation for peak pairs 2/3 <strong>and</strong> 5/6.<br />
Please see p.47 for trademark acknowledgements.<br />
19