You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
C8<br />
Mechanisms of<br />
Separation<br />
Hydrophobic binding<br />
interactions<br />
Target Analytes<br />
Analytes differing in hydrophobicity<br />
Strength of<br />
Interaction<br />
Polar, moderately polar, <strong>and</strong> non-polar analytes<br />
Uncharged acids <strong>and</strong> bases<br />
Ionized acids or bases using ion-pairing<br />
Recommended Applications<br />
Analytes differing in hydrophobicity,<br />
Strong/Moderate<br />
Homologous compounds differing by –CH 2<br />
Mixtures containing polar <strong>and</strong> very hydrophobic<br />
analytes<br />
Good starting phase for developing separation<br />
of proteins <strong>and</strong> large polypeptides.<br />
(300Å recommended)<br />
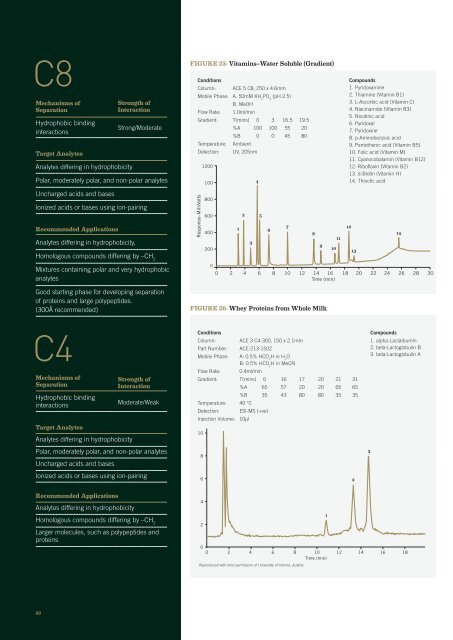
Figure 25: Vitamins–Water Soluble (Gradient)<br />
Conditions<br />
Column: ACE 5 C8, 250 x 4.6mm<br />
Mobile Phase: A. 50mM KH 2<br />
PO 4<br />
(pH 2.5)<br />
B. MeOH<br />
Flow Rate: 1.0ml/min<br />
Gradient: T(mins) 0 3 16.5 19.5<br />
%A 100 100 55 20<br />
%B 0 0 45 80<br />
Temperature: Ambient<br />
Detection: UV, 205nm<br />
Response–MilliVolts<br />
1200<br />
100<br />
800<br />
600<br />
400<br />
200<br />
0<br />
1<br />
2<br />
3<br />
4<br />
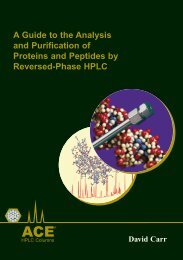
Figure 26: Whey Proteins from Whole Milk<br />
5<br />
6<br />
7<br />
8<br />
9<br />
Compounds<br />
1. Pyridoxamine<br />
2. Thiamine (Vitamin B1)<br />
3. L-Ascorbic acid (Vitamin C)<br />
4. Niacinamide (Vitamin B3)<br />
5. Nicotinic acid<br />
6. Pyridoxal<br />
7. Pyridoxine<br />
8. p-Aminobenzoic acid<br />
9. Pantothenic acid (Vitamin B5)<br />
10. Folic acid (Vitamin M)<br />
11. Cyanocobalamin (Vitamin B12)<br />
12. Riboflavin (Vitamin B2)<br />
13. d-Biotin (Vitamin H)<br />
14. Thioctic acid<br />
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30<br />
Time (min)<br />
10<br />
11<br />
12<br />
13<br />
14<br />
C4<br />
Mechanisms of<br />
Separation<br />
Hydrophobic binding<br />
interactions<br />
Target Analytes<br />
Analytes differing in hydrophobicity<br />
Strength of<br />
Interaction<br />
Moderate/Weak<br />
Polar, moderately polar, <strong>and</strong> non-polar analytes<br />
Uncharged acids <strong>and</strong> bases<br />
Ionized acids or bases using ion-pairing<br />
Conditions<br />
Column: ACE 3 C4-300, 150 x 2.1mm<br />
Part Number: ACE-213-1502<br />
Mobile Phase: A: 0.5% HCO 2<br />
H in H 2<br />
O<br />
B: 0.5% HCO 2<br />
H in MeCN<br />
Flow Rate: 0.4ml/min<br />
Gradient: T(mins) 0 16 17 20 21 31<br />
%A 65 57 20 20 65 65<br />
%B 35 43 80 80 35 35<br />
Temperature: 40 °C<br />
Detection: ESI-MS (+ve)<br />
Injection Volume: 10µl<br />
10<br />
8<br />
6<br />
2<br />
Compounds<br />
1. alpha-Lactalbumin<br />
2. beta-Lactoglobulin B<br />
3. beta-Lactoglobulin A<br />
3<br />
Recommended Applications<br />
Analytes differing in hydrophobicity<br />
Homologous compounds differing by –CH 2<br />
Larger molecules, such as polypeptides <strong>and</strong><br />
proteins<br />
4<br />
2<br />
0<br />
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18<br />
Time (min)<br />
Reproduced with kind permission of University of Vienna, Austria.<br />
1<br />
22