Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Phenyl<br />
Mechanisms of<br />
Separation<br />
π-π interactions<br />
Dipole-dipole interactions<br />
Hydrophobic binding<br />
interactions<br />
Strength of<br />
Interaction<br />
Strong<br />
Moderate<br />
Moderate<br />
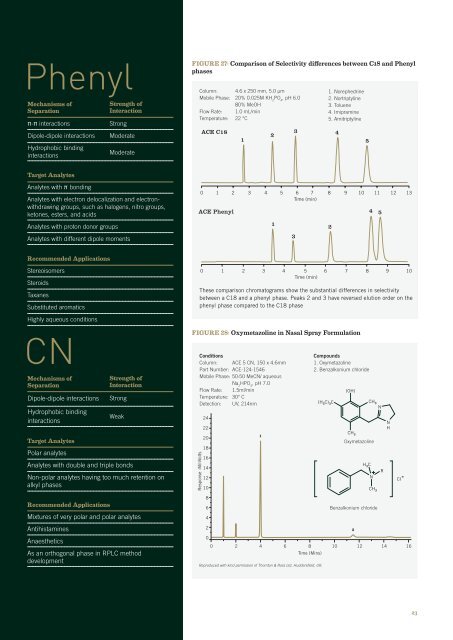
Figure 27: Comparison of Selectivity differences between C18 <strong>and</strong> Phenyl<br />
phases<br />
Column: 4.6 x 250 mm, 5.0 μm<br />
Mobile Phase: 20% 0.025M KH 2<br />
PO 4<br />
, pH 6.0<br />
80% MeOH<br />
Flow Rate: 1.0 mL/min<br />
Temperature: 22 °C<br />
ACE C18<br />
1<br />
2<br />
3 4<br />
1. Norephedrine<br />
2. Nortriptyline<br />
3. Toluene<br />
4. Imipramine<br />
5. Amitriptyline<br />
5<br />
Target Analytes<br />
Analytes with π bonding<br />
Analytes with electron delocalization <strong>and</strong> electronwithdrawing<br />
groups, such as halogens, nitro groups,<br />
ketones, esters, <strong>and</strong> acids<br />
Analytes with proton donor groups<br />
Analytes with different dipole moments<br />
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13<br />
Time (min)<br />
1<br />
3<br />
2<br />
4 5<br />
ACE Phenyl<br />
23<br />
Recommended Applications<br />
Stereoisomers<br />
Steroids<br />
Taxanes<br />
Substituted aromatics<br />
Highly aqueous conditions<br />
CN<br />
Mechanisms of<br />
Separation<br />
Dipole-dipole interactions<br />
Hydrophobic binding<br />
interactions<br />
Strength of<br />
Interaction<br />
Target Analytes<br />
Polar analytes<br />
Analytes with double <strong>and</strong> triple bonds<br />
Non-polar analytes having too much retention on<br />
alkyl phases<br />
Recommended Applications<br />
Strong<br />
Weak<br />
Mixtures of very polar <strong>and</strong> polar analytes<br />
Antihistamines<br />
Anaesthetics<br />
As an orthogonal phase in RPLC method<br />
development<br />
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10<br />
Time (min)<br />
These comparison chromatograms show the substantial differences in selectivity<br />
between a C18 <strong>and</strong> a phenyl phase. Peaks 2 <strong>and</strong> 3 have reversed elution order on the<br />
phenyl phase compared to the C18 phase<br />
Figure 28: Oxymetazoline in Nasal Spray Formulation<br />
Conditions<br />
Column: ACE 5 CN, 150 x 4.6mm<br />
Part Number: ACE-124-1546<br />
Mobile Phase: 50:50 MeCN/ aqueous<br />
Na 2<br />
HPO 4<br />
, pH 7.0<br />
Flow Rate: 1.5ml/min<br />
Temperature: 30° C<br />
Detection: UV, 214nm<br />
Response -MiliVolts<br />
24<br />
22<br />
20<br />
18<br />
16<br />
14<br />
12<br />
10<br />
8<br />
6<br />
4<br />
1<br />
Reproduced with kind permission of Thornton & Ross Ltd, Huddersfield, UK.<br />
Compounds<br />
1. Oxymetazoline<br />
2. Benzalkonium chloride<br />
(H 3 C) 3 C<br />
CH 3<br />
Oxymetazoline<br />
2<br />
2<br />
0<br />
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16<br />
Time (Mins)<br />
(OH)<br />
H 3 C<br />
CH 3<br />
N<br />
N<br />
CH 3<br />
Benzalkonium chloride<br />
R<br />
N<br />
H<br />
CI