Innovative Secondary Education For Skills Enhancement
Innovative Secondary Education For Skills Enhancement
Innovative Secondary Education For Skills Enhancement
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Comparisons and<br />
Conclusions<br />
Prior to beginning this work, the project team anticipated<br />
that the skills sought by employers would differ by region<br />
or by per capita income. We also thought that there might<br />
be important differences between the skills required by<br />
large employers and those sought by SMEs.<br />
And indeed there are some minor regional and level-ofdevelopment<br />
differences. What is striking, however, is the<br />
convergence across Africa and Asia of the importance of<br />
basic cognitive skills, of non-cognitive or “soft” or “life”<br />
skills, and of technical skills. What is also striking is the<br />
crucial importance of non-cognitive skills for the informal<br />
economy, an area that has been generally neglected in all<br />
the attention given to skills in recent years. Clearly, given<br />
that women are more likely than men to be employed<br />
in the informal economy, even more attention should be<br />
devoted to non-cognitive skills education for girls than for<br />
boys in secondary school.<br />
The background research papers do not throw any light<br />
on possible differences between large employers and<br />
SMEs or between urban and rural areas, except that informal<br />
employment is more pervasive in rural zones. These<br />
topics will be developed in the final version of this paper,<br />
depending on the availability of information.<br />
While the ISESE project is not trying to draw up a precise<br />
blueprint of what should be done, the research reported<br />
in this section does indicate that the skill set required by<br />
employers, both formal and informal, should now likely<br />
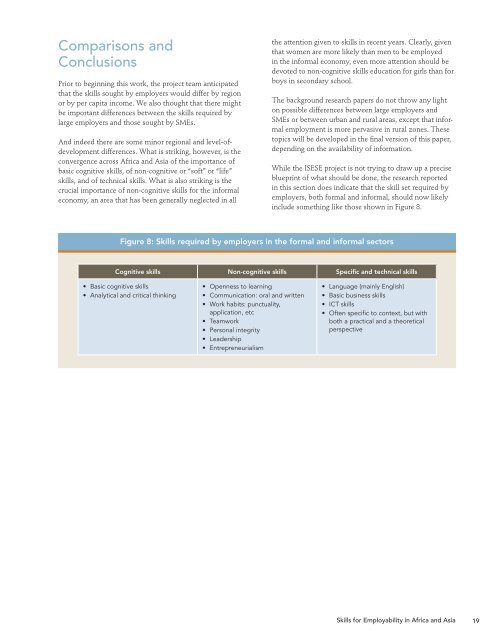
include something like those shown in Figure 8.<br />
Figure 8: <strong>Skills</strong> required by employers in the formal and informal sectors<br />
Cognitive skills Non-cognitive skills Specific and technical skills<br />
• Basic cognitive skills<br />
• Analytical and critical thinking<br />
• Openness to learning<br />
• Communication: oral and written<br />
• Work habits: punctuality,<br />
application, etc<br />
• Teamwork<br />
• Personal integrity<br />
• Leadership<br />
• Entrepreneurialism<br />
• Language (mainly English)<br />
• Basic business skills<br />
• ICT skills<br />
• Often specific to context, but with<br />
both a practical and a theoretical<br />
perspective<br />
<strong>Skills</strong> for Employability in Africa and Asia 19