4th International Conference on Principles and Practices ... - MADOC
4th International Conference on Principles and Practices ... - MADOC
4th International Conference on Principles and Practices ... - MADOC
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Derivative<br />
C<strong>on</strong>tract<br />
Comp<strong>on</strong>ent<br />
Repository<br />
Removing the c<strong>on</strong>stant<br />
lower bound<br />
Silver price as<br />
lower bound<br />
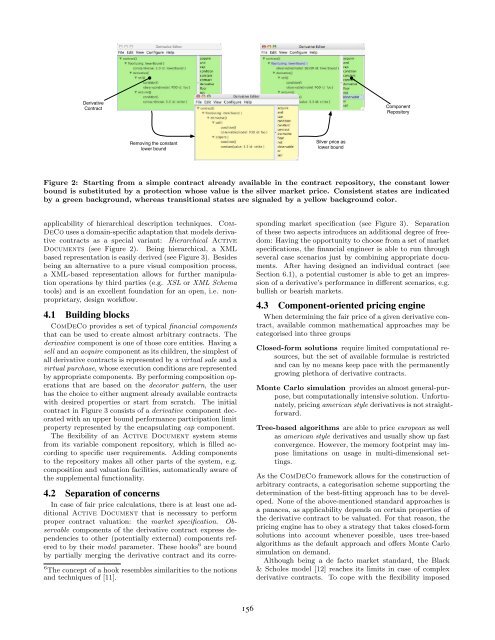
Figure 2: Starting from a simple c<strong>on</strong>tract already available in the c<strong>on</strong>tract repository, the c<strong>on</strong>stant lower<br />
bound is substituted by a protecti<strong>on</strong> whose value is the silver market price. C<strong>on</strong>sistent states are indicated<br />
by a green background, whereas transiti<strong>on</strong>al states are signaled by a yellow background color.<br />
applicability of hierarchical descripti<strong>on</strong> techniques. Com-<br />
DeCo uses a domain-specific adaptati<strong>on</strong> that models derivative<br />
c<strong>on</strong>tracts as a special variant: Hierarchical Active<br />
Documents (see Figure 2). Being hierarchical, a XML<br />
based representati<strong>on</strong> is easily derived (see Figure 3). Besides<br />
being an alternative to a pure visual compositi<strong>on</strong> process,<br />
a XML-based representati<strong>on</strong> allows for further manipulati<strong>on</strong><br />
operati<strong>on</strong>s by third parties (e.g. XSL or XML Schema<br />
tools) <strong>and</strong> is an excellent foundati<strong>on</strong> for an open, i.e. n<strong>on</strong>proprietary,<br />
design workflow.<br />
4.1 Building blocks<br />
ComDeCo provides a set of typical financial comp<strong>on</strong>ents<br />
that can be used to create almost arbitrary c<strong>on</strong>tracts. The<br />
derivative comp<strong>on</strong>ent is <strong>on</strong>e of those core entities. Having a<br />
sell <strong>and</strong> an acquire comp<strong>on</strong>ent as its children, the simplest of<br />
all derivative c<strong>on</strong>tracts is represented by a virtual sale <strong>and</strong> a<br />
virtual purchase, whose executi<strong>on</strong> c<strong>on</strong>diti<strong>on</strong>s are represented<br />
by appropriate comp<strong>on</strong>ents. By performing compositi<strong>on</strong> operati<strong>on</strong>s<br />
that are based <strong>on</strong> the decorator pattern, the user<br />
has the choice to either augment already available c<strong>on</strong>tracts<br />
with desired properties or start from scratch. The initial<br />
c<strong>on</strong>tract in Figure 3 c<strong>on</strong>sists of a derivative comp<strong>on</strong>ent decorated<br />
with an upper bound performance participati<strong>on</strong> limit<br />
property represented by the encapsulating cap comp<strong>on</strong>ent.<br />
The flexibility of an Active Document system stems<br />
from its variable comp<strong>on</strong>ent repository, which is filled according<br />
to specific user requirements. Adding comp<strong>on</strong>ents<br />
to the repository makes all other parts of the system, e.g.<br />
compositi<strong>on</strong> <strong>and</strong> valuati<strong>on</strong> facilities, automatically aware of<br />
the supplemental functi<strong>on</strong>ality.<br />
4.2 Separati<strong>on</strong> of c<strong>on</strong>cerns<br />
In case of fair price calculati<strong>on</strong>s, there is at least <strong>on</strong>e additi<strong>on</strong>al<br />
Active Document that is necessary to perform<br />
proper c<strong>on</strong>tract valuati<strong>on</strong>: the market specificati<strong>on</strong>. Observable<br />
comp<strong>on</strong>ents of the derivative c<strong>on</strong>tract express dependencies<br />
to other (potentially external) comp<strong>on</strong>ents refered<br />
to by their model parameter. These hooks 6 are bound<br />
by partially merging the derivative c<strong>on</strong>tract <strong>and</strong> its corre-<br />
6 The c<strong>on</strong>cept of a hook resembles similarities to the noti<strong>on</strong>s<br />
<strong>and</strong> techniques of [11].<br />
sp<strong>on</strong>ding market specificati<strong>on</strong> (see Figure 3). Separati<strong>on</strong><br />
of these two aspects introduces an additi<strong>on</strong>al degree of freedom:<br />
Having the opportunity to choose from a set of market<br />
specificati<strong>on</strong>s, the financial engineer is able to run through<br />
several case scenarios just by combining appropriate documents.<br />
After having designed an individual c<strong>on</strong>tract (see<br />
Secti<strong>on</strong> 6.1), a potential customer is able to get an impressi<strong>on</strong><br />
of a derivative’s performance in different scenarios, e.g.<br />
bullish or bearish markets.<br />
4.3 Comp<strong>on</strong>ent-oriented pricing engine<br />
When determining the fair price of a given derivative c<strong>on</strong>tract,<br />
available comm<strong>on</strong> mathematical approaches may be<br />
categorised into three groups<br />
Closed-form soluti<strong>on</strong>s require limited computati<strong>on</strong>al resources,<br />
but the set of available formulae is restricted<br />
<strong>and</strong> can by no means keep pace with the permanently<br />
growing plethora of derivative c<strong>on</strong>tracts.<br />
M<strong>on</strong>te Carlo simulati<strong>on</strong> provides an almost general-purpose,<br />
but computati<strong>on</strong>ally intensive soluti<strong>on</strong>. Unfortunately,<br />
pricing american style derivatives is not straightforward.<br />
Tree-based algorithms are able to price european as well<br />
as american style derivatives <strong>and</strong> usually show up fast<br />
c<strong>on</strong>vergence. However, the memory footprint may impose<br />
limitati<strong>on</strong>s <strong>on</strong> usage in multi-dimensi<strong>on</strong>al settings.<br />
As the ComDeCo framework allows for the c<strong>on</strong>structi<strong>on</strong> of<br />
arbitrary c<strong>on</strong>tracts, a categorisati<strong>on</strong> scheme supporting the<br />
determinati<strong>on</strong> of the best-fitting approach has to be developed.<br />
N<strong>on</strong>e of the above-menti<strong>on</strong>ed st<strong>and</strong>ard approaches is<br />
a panacea, as applicability depends <strong>on</strong> certain properties of<br />
the derivative c<strong>on</strong>tract to be valuated. For that reas<strong>on</strong>, the<br />
pricing engine has to obey a strategy that takes closed-form<br />
soluti<strong>on</strong>s into account whenever possible, uses tree-based<br />
algorithms as the default approach <strong>and</strong> offers M<strong>on</strong>te Carlo<br />
simulati<strong>on</strong> <strong>on</strong> dem<strong>and</strong>.<br />
Although being a de facto market st<strong>and</strong>ard, the Black<br />
& Scholes model [12] reaches its limits in case of complex<br />
derivative c<strong>on</strong>tracts. To cope with the flexibility imposed<br />
156