Sustainability of rice in the global food system - IRRI books
Sustainability of rice in the global food system - IRRI books
Sustainability of rice in the global food system - IRRI books
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
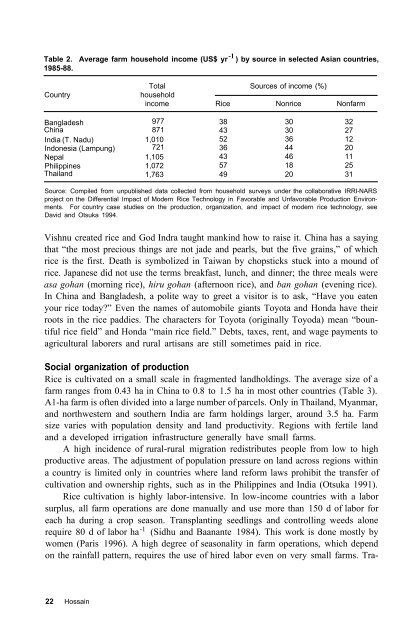
Table 2. Average farm household <strong>in</strong>come (US$ yr<br />
-1<br />
) by source <strong>in</strong> selected Asian countries,<br />
1985-88.<br />
Country<br />
Total Sources <strong>of</strong> <strong>in</strong>come (%)<br />
household<br />
<strong>in</strong>come Rice Non<strong>rice</strong> Nonfarm<br />
Bangladesh 977 38 30 32<br />
Ch<strong>in</strong>a 871 43 30 27<br />
India (T. Nadu) 1,010 52 36 12<br />
Indonesia (Lampung) 721 36 44 20<br />
Nepal 1,105 43 46 11<br />
Philipp<strong>in</strong>es 1,072 57 18 25<br />
Thailand 1,763 49 20 31<br />
Source: Compiled from unpublished data collected from household surveys under <strong>the</strong> collaborative <strong>IRRI</strong>-NARS<br />
project on <strong>the</strong> Differential Impact <strong>of</strong> Modern Rice Technology <strong>in</strong> Favorable and Unfavorable Production Environments.<br />
For country case studies on <strong>the</strong> production, organization, and impact <strong>of</strong> modern <strong>rice</strong> technology, see<br />
David and Otsuka 1994.<br />
Vishnu created <strong>rice</strong> and God Indra taught mank<strong>in</strong>d how to raise it. Ch<strong>in</strong>a has a say<strong>in</strong>g<br />
that “<strong>the</strong> most precious th<strong>in</strong>gs are not jade and pearls, but <strong>the</strong> five gra<strong>in</strong>s,” <strong>of</strong> which<br />
<strong>rice</strong> is <strong>the</strong> first. Death is symbolized <strong>in</strong> Taiwan by chopsticks stuck <strong>in</strong>to a mound <strong>of</strong><br />
<strong>rice</strong>. Japanese did not use <strong>the</strong> terms breakfast, lunch, and d<strong>in</strong>ner; <strong>the</strong> three meals were<br />
asa gohan (morn<strong>in</strong>g <strong>rice</strong>), hiru gohan (afternoon <strong>rice</strong>), and ban gohan (even<strong>in</strong>g <strong>rice</strong>).<br />
In Ch<strong>in</strong>a and Bangladesh, a polite way to greet a visitor is to ask, “Have you eaten<br />
your <strong>rice</strong> today” Even <strong>the</strong> names <strong>of</strong> automobile giants Toyota and Honda have <strong>the</strong>ir<br />
roots <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>rice</strong> paddies. The characters for Toyota (orig<strong>in</strong>ally Toyoda) mean “bountiful<br />
<strong>rice</strong> field” and Honda “ma<strong>in</strong> <strong>rice</strong> field.” Debts, taxes, rent, and wage payments to<br />
agricultural laborers and rural artisans are still sometimes paid <strong>in</strong> <strong>rice</strong>.<br />
Social organization <strong>of</strong> production<br />
Rice is cultivated on a small scale <strong>in</strong> fragmented landhold<strong>in</strong>gs. The average size <strong>of</strong> a<br />
farm ranges from 0.43 ha <strong>in</strong> Ch<strong>in</strong>a to 0.8 to 1.5 ha <strong>in</strong> most o<strong>the</strong>r countries (Table 3).<br />
A1-ha farm is <strong>of</strong>ten divided <strong>in</strong>to a large number <strong>of</strong> parcels. Only <strong>in</strong> Thailand, Myanmar,<br />
and northwestern and sou<strong>the</strong>rn India are farm hold<strong>in</strong>gs larger, around 3.5 ha. Farm<br />
size varies with population density and land productivity. Regions with fertile land<br />
and a developed irrigation <strong>in</strong>frastructure generally have small farms.<br />
A high <strong>in</strong>cidence <strong>of</strong> rural-rural migration redistributes people from low to high<br />
productive areas. The adjustment <strong>of</strong> population pressure on land across regions with<strong>in</strong><br />
a country is limited only <strong>in</strong> countries where land reform laws prohibit <strong>the</strong> transfer <strong>of</strong><br />
cultivation and ownership rights, such as <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> Philipp<strong>in</strong>es and India (Otsuka 1991).<br />
Rice cultivation is highly labor-<strong>in</strong>tensive. In low-<strong>in</strong>come countries with a labor<br />
surplus, all farm operations are done manually and use more than 150 d <strong>of</strong> labor for<br />
each ha dur<strong>in</strong>g a crop season. Transplant<strong>in</strong>g seedl<strong>in</strong>gs and controll<strong>in</strong>g weeds alone<br />
require 80 d <strong>of</strong> labor ha -1 (Sidhu and Baanante 1984). This work is done mostly by<br />
women (Paris 1996). A high degree <strong>of</strong> seasonality <strong>in</strong> farm operations, which depend<br />
on <strong>the</strong> ra<strong>in</strong>fall pattern, requires <strong>the</strong> use <strong>of</strong> hired labor even on very small farms. Tra-<br />
22 Hossa<strong>in</strong>