Pediatric Clinics of North America - CIPERJ
Pediatric Clinics of North America - CIPERJ
Pediatric Clinics of North America - CIPERJ
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
DECISION ANALYSIS IN PEDIATRIC HEMATOLOGY<br />
291<br />
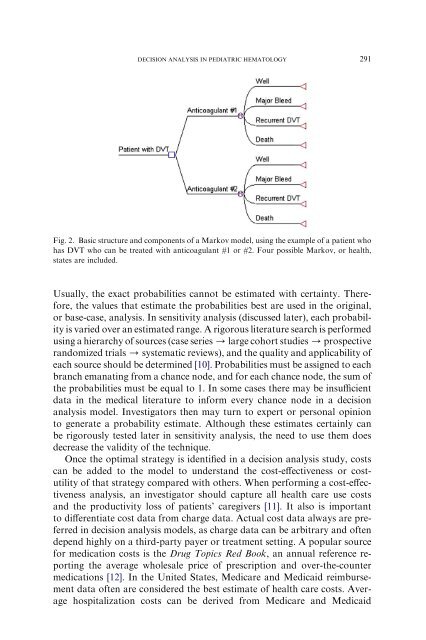
Fig. 2. Basic structure and components <strong>of</strong> a Markov model, using the example <strong>of</strong> a patient who<br />
has DVT who can be treated with anticoagulant #1 or #2. Four possible Markov, or health,<br />
states are included.<br />
Usually, the exact probabilities cannot be estimated with certainty. Therefore,<br />
the values that estimate the probabilities best are used in the original,<br />
or base-case, analysis. In sensitivity analysis (discussed later), each probability<br />
is varied over an estimated range. A rigorous literature search is performed<br />
using a hierarchy <strong>of</strong> sources (case series / large cohort studies / prospective<br />
randomized trials / systematic reviews), and the quality and applicability <strong>of</strong><br />
each source should be determined [10]. Probabilities must be assigned to each<br />
branch emanating from a chance node, and for each chance node, the sum <strong>of</strong><br />
the probabilities must be equal to 1. In some cases there may be insufficient<br />
data in the medical literature to inform every chance node in a decision<br />
analysis model. Investigators then may turn to expert or personal opinion<br />
to generate a probability estimate. Although these estimates certainly can<br />
be rigorously tested later in sensitivity analysis, the need to use them does<br />
decrease the validity <strong>of</strong> the technique.<br />
Once the optimal strategy is identified in a decision analysis study, costs<br />
can be added to the model to understand the cost-effectiveness or costutility<br />
<strong>of</strong> that strategy compared with others. When performing a cost-effectiveness<br />
analysis, an investigator should capture all health care use costs<br />
and the productivity loss <strong>of</strong> patients’ caregivers [11]. It also is important<br />
to differentiate cost data from charge data. Actual cost data always are preferred<br />
in decision analysis models, as charge data can be arbitrary and <strong>of</strong>ten<br />
depend highly on a third-party payer or treatment setting. A popular source<br />
for medication costs is the Drug Topics Red Book, an annual reference reporting<br />
the average wholesale price <strong>of</strong> prescription and over-the-counter<br />
medications [12]. In the United States, Medicare and Medicaid reimbursement<br />
data <strong>of</strong>ten are considered the best estimate <strong>of</strong> health care costs. Average<br />
hospitalization costs can be derived from Medicare and Medicaid