Department of Strategy and Donor Coordination
Department of Strategy and Donor Coordination
Department of Strategy and Donor Coordination
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
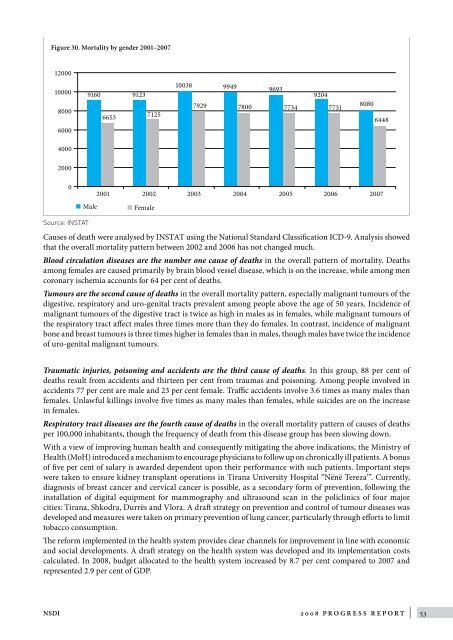
Figure 30. Mortality by gender 2001–2007<br />
12000<br />
10000<br />
8000<br />
6000<br />
9160 9123<br />
6653<br />
7125<br />
10038 9949 9693<br />
9204<br />
7929 7800 7734 7731<br />
8080<br />
6448<br />
4000<br />
2000<br />
0<br />
Male<br />
2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007<br />
Female<br />
Source: INSTAT<br />
Causes <strong>of</strong> death were analysed by INSTAT using the National St<strong>and</strong>ard Classification ICD-9. Analysis showed<br />
that the overall mortality pattern between 2002 <strong>and</strong> 2006 has not changed much.<br />
Blood circulation diseases are the number one cause <strong>of</strong> deaths in the overall pattern <strong>of</strong> mortality. Deaths<br />
among females are caused primarily by brain blood vessel disease, which is on the increase, while among men<br />
coronary ischemia accounts for 64 per cent <strong>of</strong> deaths.<br />
Tumours are the second cause <strong>of</strong> deaths in the overall mortality pattern, especially malignant tumours <strong>of</strong> the<br />
digestive, respiratory <strong>and</strong> uro-genital tracts prevalent among people above the age <strong>of</strong> 50 years. Incidence <strong>of</strong><br />
malignant tumours <strong>of</strong> the digestive tract is twice as high in males as in females, while malignant tumours <strong>of</strong><br />
the respiratory tract affect males three times more than they do females. In contrast, incidence <strong>of</strong> malignant<br />
bone <strong>and</strong> breast tumours is three times higher in females than in males, though males have twice the incidence<br />
<strong>of</strong> uro-genital malignant tumours.<br />
Traumatic injuries, poisoning <strong>and</strong> accidents are the third cause <strong>of</strong> deaths. In this group, 88 per cent <strong>of</strong><br />
deaths result from accidents <strong>and</strong> thirteen per cent from traumas <strong>and</strong> poisoning. Among people involved in<br />
accidents 77 per cent are male <strong>and</strong> 23 per cent female. Traffic accidents involve 3.6 times as many males than<br />
females. Unlawful killings involve five times as many males than females, while suicides are on the increase<br />
in females.<br />
Respiratory tract diseases are the fourth cause <strong>of</strong> deaths in the overall mortality pattern <strong>of</strong> causes <strong>of</strong> deaths<br />
per 100,000 inhabitants, though the frequency <strong>of</strong> death from this disease group has been slowing down.<br />
With a view <strong>of</strong> improving human health <strong>and</strong> consequently mitigating the above indications, the Ministry <strong>of</strong><br />
Health (MoH) introduced a mechanism to encourage physicians to follow up on chronically ill patients. A bonus<br />
<strong>of</strong> five per cent <strong>of</strong> salary is awarded dependent upon their performance with such patients. Important steps<br />
were taken to ensure kidney transplant operations in Tirana University Hospital “Nënë Tereza’”. Currently,<br />
diagnosis <strong>of</strong> breast cancer <strong>and</strong> cervical cancer is possible, as a secondary form <strong>of</strong> prevention, following the<br />
installation <strong>of</strong> digital equipment for mammography <strong>and</strong> ultrasound scan in the policlinics <strong>of</strong> four major<br />
cities: Tirana, Shkodra, Durrës <strong>and</strong> Vlora. A draft strategy on prevention <strong>and</strong> control <strong>of</strong> tumour diseases was<br />
developed <strong>and</strong> measures were taken on primary prevention <strong>of</strong> lung cancer, particularly through efforts to limit<br />
tobacco consumption.<br />
The reform implemented in the health system provides clear channels for improvement in line with economic<br />
<strong>and</strong> social developments. A draft strategy on the health system was developed <strong>and</strong> its implementation costs<br />
calculated. In 2008, budget allocated to the health system increased by 8.7 per cent compared to 2007 <strong>and</strong><br />
represented 2.9 per cent <strong>of</strong> GDP.<br />
NSDI 2008 Progress Report | 53