acta facultatis educationis physicae universitatis comenianae
acta facultatis educationis physicae universitatis comenianae
acta facultatis educationis physicae universitatis comenianae
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
The subjective exercise experiences and aesthetic activities<br />
9<br />
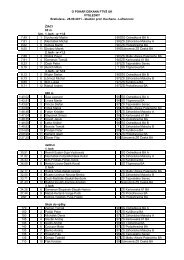
Figure 1<br />
T-test differences calculated before and after physical activity in fatigue (F),<br />
Positive well being (PMB) and Psychological distress (PD) for aesthetic and non aesthetic<br />
group separately<br />
*Denote significant differences<br />
T-test for depended samples was calculated before and after physical activity in Fatigue<br />
(F), Positive well being (PMB) and Psychological distress (PD) for aesthetic and non aesthetic<br />
group separately and is presented in Figure 1. The results in PWB were significantly higher<br />
after physical activity (Mean = 22.9) than before physical activity (Mean = 20.9) with aesthetic<br />
content. Significant differences before and after physical activity for PD and F in both groups<br />
and for PWB in non-aesthetic group were not found.<br />
Discussion<br />
In accordance with the first aim of investigation the evidence of reliability and validity<br />
of SEES were provided. The four-factor structure of SEES subscales obtained by Mc Auley<br />
& Courneya (1994) was repeated in this study. If we presume that construct validity<br />
as an association between the test scores and the prediction of a theoretical trait, the SEES<br />
questionnaire could be considered validated for stabile four-factor structure. However, any<br />
threats to the reliability (or consistency) of a test are also threats to its validity because a test<br />
cannot be said to be any more systematically valid than it is first systematic or consistent.<br />
According to Cronbach alpha coefficients, the internal consistency of SEES subscale was<br />
high and satisfactory, similar to those presented by Mc Auley & Courneya (1994). Obtained<br />
differences in initially collected data were significant for PWB and F in favour of aesthetic<br />
group. The mean pre-exercise scores (for PWB subscale) in this study for aesthetic group<br />
were higher than pre-exercise scores in study of Mc Auley & Courneya (1994), and lower<br />
in non-aesthetic group. The mean pre-exercise scores in aesthetic group for all three subscales<br />
(PWB, PD and F) were generally higher than in previous investigations. The mean scores<br />
obtained in non-aesthetic group were more coherent with previously obtained results. Nevertheless,<br />
the significant differences in PWB before and after exercise were noted in this study<br />
only in aesthetic group meaning that aesthetic contents in training effect positively on male<br />
students population. Consequently, the initially obtained differences between groups do not<br />
Acta Facultatis Educationis Physicae Universitatis Comenianae LII/I