Wind Turbine
Wind Turbine
Wind Turbine
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
chemical<br />
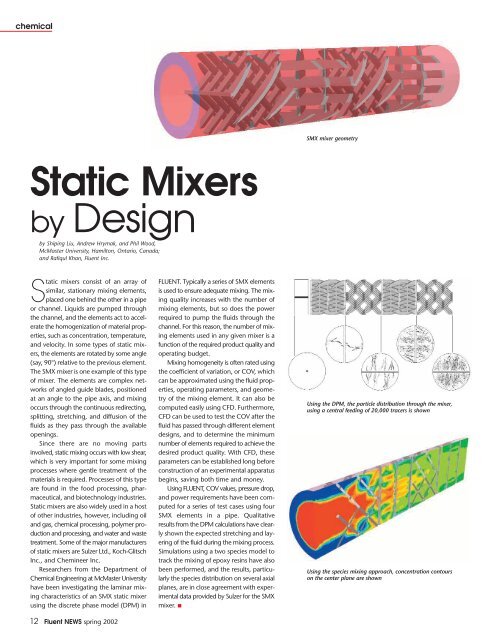
SMX mixer geometry<br />
Static Mixers<br />
by Design<br />
by Shiping Liu, Andrew Hrymak, and Phil Wood,<br />
McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada;<br />
and Rafiqul Khan, Fluent Inc.<br />
Static mixers consist of an array of<br />
similar, stationary mixing elements,<br />
placed one behind the other in a pipe<br />
or channel. Liquids are pumped through<br />
the channel, and the elements act to accelerate<br />
the homogenization of material properties,<br />
such as concentration, temperature,<br />
and velocity. In some types of static mixers,<br />
the elements are rotated by some angle<br />
(say, 90°) relative to the previous element.<br />
The SMX mixer is one example of this type<br />
of mixer. The elements are complex networks<br />
of angled guide blades, positioned<br />
at an angle to the pipe axis, and mixing<br />
occurs through the continuous redirecting,<br />
splitting, stretching, and diffusion of the<br />
fluids as they pass through the available<br />
openings.<br />
Since there are no moving parts<br />
involved, static mixing occurs with low shear,<br />
which is very important for some mixing<br />
processes where gentle treatment of the<br />
materials is required. Processes of this type<br />
are found in the food processing, pharmaceutical,<br />
and biotechnology industries.<br />
Static mixers are also widely used in a host<br />
of other industries, however, including oil<br />
and gas, chemical processing, polymer production<br />
and processing, and water and waste<br />
treatment. Some of the major manufacturers<br />
of static mixers are Sulzer Ltd., Koch-Glitsch<br />
Inc., and Chemineer Inc.<br />
Researchers from the Department of<br />
Chemical Engineering at McMaster University<br />
have been investigating the laminar mixing<br />
characteristics of an SMX static mixer<br />
using the discrete phase model (DPM) in<br />
FLUENT. Typically a series of SMX elements<br />
is used to ensure adequate mixing. The mixing<br />
quality increases with the number of<br />
mixing elements, but so does the power<br />
required to pump the fluids through the<br />
channel. For this reason, the number of mixing<br />
elements used in any given mixer is a<br />
function of the required product quality and<br />
operating budget.<br />
Mixing homogeneity is often rated using<br />
the coefficient of variation, or COV, which<br />
can be approximated using the fluid properties,<br />
operating parameters, and geometry<br />
of the mixing element. It can also be<br />
computed easily using CFD. Furthermore,<br />
CFD can be used to test the COV after the<br />
fluid has passed through different element<br />
designs, and to determine the minimum<br />
number of elements required to achieve the<br />
desired product quality. With CFD, these<br />
parameters can be established long before<br />
construction of an experimental apparatus<br />
begins, saving both time and money.<br />
Using FLUENT, COV values, pressure drop,<br />
and power requirements have been computed<br />
for a series of test cases using four<br />
SMX elements in a pipe. Qualitative<br />
results from the DPM calculations have clearly<br />
shown the expected stretching and layering<br />
of the fluid during the mixing process.<br />
Simulations using a two species model to<br />
track the mixing of epoxy resins have also<br />
been performed, and the results, particularly<br />
the species distribution on several axial<br />
planes, are in close agreement with experimental<br />
data provided by Sulzer for the SMX<br />
mixer. ■<br />
Using the DPM, the particle distribution through the mixer,<br />
using a central feeding of 20,000 tracers is shown<br />
Using the species mixing approach, concentration contours<br />
on the center plane are shown<br />
12 Fluent NEWS spring 2002