Download - Yang-Sheng
Download - Yang-Sheng
Download - Yang-Sheng
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
The brain is surrounded and protected by the<br />
rigid, bony skull and three membranes, called meninges.<br />
The tough, fibrous outer membrane is the<br />
dura mater. The archanoid, the intermediate membrane,<br />
is web-like. The pia mater is the innermost<br />
covering and is the most delicate. It is molded to the<br />
shape of the brain. The cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)<br />
surrounds the brain and spinal cord. It flows<br />
through open chambers in the brain, called ventricles,<br />
and out an opening to the spinal cord. The<br />
brain actually floats in the shock-absorbing CSF,<br />
and is thus protected from trauma. The CSF also<br />
brings nutrients to the brain and removes wastes.<br />
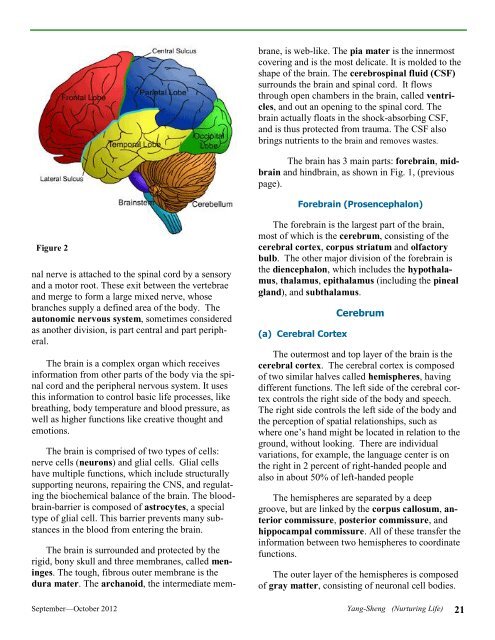
The brain has 3 main parts: forebrain, midbrain<br />
and hindbrain, as shown in Fig. 1, (previous<br />
page).<br />
Forebrain (Prosencephalon)<br />
Figure 2<br />
nal nerve is attached to the spinal cord by a sensory<br />
and a motor root. These exit between the vertebrae<br />
and merge to form a large mixed nerve, whose<br />
branches supply a defined area of the body. The<br />
autonomic nervous system, sometimes considered<br />
as another division, is part central and part peripheral.<br />
The brain is a complex organ which receives<br />
information from other parts of the body via the spinal<br />
cord and the peripheral nervous system. It uses<br />
this information to control basic life processes, like<br />
breathing, body temperature and blood pressure, as<br />
well as higher functions like creative thought and<br />
emotions.<br />
The brain is comprised of two types of cells:<br />
nerve cells (neurons) and glial cells. Glial cells<br />
have multiple functions, which include structurally<br />
supporting neurons, repairing the CNS, and regulating<br />
the biochemical balance of the brain. The bloodbrain-barrier<br />
is composed of astrocytes, a special<br />
type of glial cell. This barrier prevents many substances<br />
in the blood from entering the brain.<br />
The forebrain is the largest part of the brain,<br />
most of which is the cerebrum, consisting of the<br />
cerebral cortex, corpus striatum and olfactory<br />
bulb. The other major division of the forebrain is<br />
the diencephalon, which includes the hypothalamus,<br />
thalamus, epithalamus (including the pineal<br />
gland), and subthalamus.<br />
(a) Cerebral Cortex<br />
Cerebrum<br />
The outermost and top layer of the brain is the<br />
cerebral cortex. The cerebral cortex is composed<br />
of two similar halves called hemispheres, having<br />
different functions. The left side of the cerebral cortex<br />
controls the right side of the body and speech.<br />
The right side controls the left side of the body and<br />
the perception of spatial relationships, such as<br />
where one’s hand might be located in relation to the<br />
ground, without looking. There are individual<br />
variations, for example, the language center is on<br />
the right in 2 percent of right-handed people and<br />
also in about 50% of left-handed people<br />
The hemispheres are separated by a deep<br />
groove, but are linked by the corpus callosum, anterior<br />
commissure, posterior commissure, and<br />
hippocampal commissure. All of these transfer the<br />
information between two hemispheres to coordinate<br />
functions.<br />
The outer layer of the hemispheres is composed<br />
of gray matter, consisting of neuronal cell bodies.<br />
September—October 2012 <strong>Yang</strong>-<strong>Sheng</strong> (Nurturing Life) 21