Surface treatment of metals using an atmospheric pressure plasma ...
Surface treatment of metals using an atmospheric pressure plasma ...
Surface treatment of metals using an atmospheric pressure plasma ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
844 M.C. Kim et al. / <strong>Surface</strong> <strong>an</strong>d Coatings Technology 174 –175 (2003) 839–844<br />
highly activated surfaces were obtained <strong>an</strong>d had short<br />
duration time <strong>of</strong> approximately 15 h at air environment<br />
after <strong>plasma</strong> treating. Based on our experimental data,<br />
we could underst<strong>an</strong>d the surface phenomena caused by<br />
the role <strong>of</strong> oxygen <strong>an</strong>d nitrogen gases. We also confirm<br />
that the <strong>metals</strong> could be easily treated to cle<strong>an</strong> <strong>an</strong>d even<br />
new particles could be aggregated densely on metal<br />
surfaces under the air condition by <strong>atmospheric</strong> <strong>plasma</strong><br />
jet method.<br />
Acknowledgments<br />
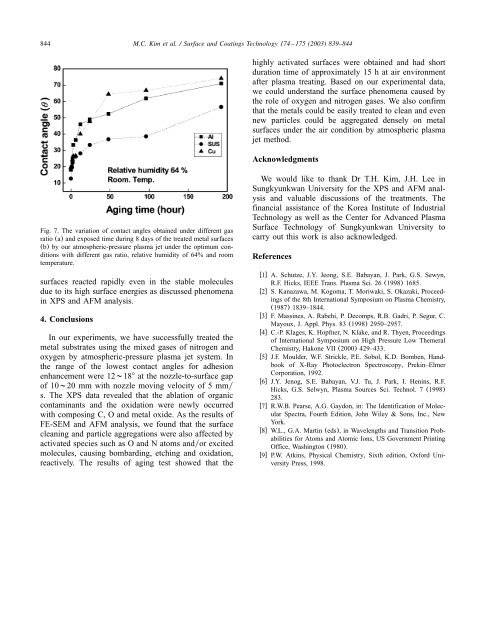
Fig. 7. The variation <strong>of</strong> contact <strong>an</strong>gles obtained under different gas<br />
ratio (a) <strong>an</strong>d exposed time during 8 days <strong>of</strong> the treated metal surfaces<br />
(b) by our <strong>atmospheric</strong>-<strong>pressure</strong> <strong>plasma</strong> jet under the optimum conditions<br />
with different gas ratio, relative humidity <strong>of</strong> 64% <strong>an</strong>d room<br />
temperature.<br />
surfaces reacted rapidly even in the stable molecules<br />
due to its high surface energies as discussed phenomena<br />
in XPS <strong>an</strong>d AFM <strong>an</strong>alysis.<br />
4. Conclusions<br />
In our experiments, we have successfully treated the<br />
metal substrates <strong>using</strong> the mixed gases <strong>of</strong> nitrogen <strong>an</strong>d<br />
oxygen by <strong>atmospheric</strong>-<strong>pressure</strong> <strong>plasma</strong> jet system. In<br />
the r<strong>an</strong>ge <strong>of</strong> the lowest contact <strong>an</strong>gles for adhesion<br />
enh<strong>an</strong>cement were 12;188 at the nozzle-to-surface gap<br />
<strong>of</strong> 10;20 mm with nozzle moving velocity <strong>of</strong> 5 mmy<br />
s. The XPS data revealed that the ablation <strong>of</strong> org<strong>an</strong>ic<br />
contamin<strong>an</strong>ts <strong>an</strong>d the oxidation were newly occurred<br />
with composing C, O <strong>an</strong>d metal oxide. As the results <strong>of</strong><br />
FE-SEM <strong>an</strong>d AFM <strong>an</strong>alysis, we found that the surface<br />
cle<strong>an</strong>ing <strong>an</strong>d particle aggregations were also affected by<br />
activated species such as O <strong>an</strong>d N atoms <strong>an</strong>dyor excited<br />
molecules, ca<strong>using</strong> bombarding, etching <strong>an</strong>d oxidation,<br />
reactively. The results <strong>of</strong> aging test showed that the<br />
We would like to th<strong>an</strong>k Dr T.H. Kim, J.H. Lee in<br />
Sungkyunkw<strong>an</strong> University for the XPS <strong>an</strong>d AFM <strong>an</strong>alysis<br />
<strong>an</strong>d valuable discussions <strong>of</strong> the <strong>treatment</strong>s. The<br />
fin<strong>an</strong>cial assist<strong>an</strong>ce <strong>of</strong> the Korea Institute <strong>of</strong> Industrial<br />
Technology as well as the Center for Adv<strong>an</strong>ced Plasma<br />
<strong>Surface</strong> Technology <strong>of</strong> Sungkyunkw<strong>an</strong> University to<br />
carry out this work is also acknowledged.<br />
References<br />
w1x A. Schutze, J.Y. Jeong, S.E. Babay<strong>an</strong>, J. Park, G.S. Sewyn,<br />
R.F. Hicks, IEEE Tr<strong>an</strong>s. Plasma Sci. 26 (1998) 1685.<br />
w2x S. K<strong>an</strong>azawa, M. Kogoma, T. Moriwaki, S. Okazaki, Proceedings<br />
<strong>of</strong> the 8th International Symposium on Plasma Chemistry,<br />
(1987) 1839–1844.<br />
w3x F. Massines, A. Rabehi, P. Decomps, R.B. Gadri, P. Segur, C.<br />
Mayoux, J. Appl. Phys. 83 (1998) 2950–2957.<br />
w4x C.-P. Klages, K. Hopfner, N. Klake, <strong>an</strong>d R. Thyen, Proceedings<br />
<strong>of</strong> International Symposium on High Pressure Low Themeral<br />
Chemistry, Hakone VII (2000) 429–433.<br />
w5x J.F. Moulder, W.F. Strickle, P.E. Sobol, K.D. Bomben, H<strong>an</strong>dbook<br />
<strong>of</strong> X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy, Prekin–Elmer<br />
Corporation, 1992.<br />
w6x J.Y. Jenog, S.E. Babay<strong>an</strong>, V.J. Tu, J. Park, I. Henins, R.F.<br />
Hicks, G.S. Selwyn, Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 7 (1998)<br />
283.<br />
w7x R.W.B. Pearse, A.G. Gaydon, in: The Identification <strong>of</strong> Molecular<br />
Spectra, Fourth Edition, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New<br />
York.<br />
w8x W.L., G.A. Martin (eds), in Wavelengths <strong>an</strong>d Tr<strong>an</strong>sition Probabilities<br />
for Atoms <strong>an</strong>d Atomic Ions, US Government Printing<br />
Office, Washington (1980).<br />
w9x P.W. Atkins, Physical Chemistry, Sixth edition, Oxford University<br />
Press, 1998.