OLSG Report_Final_06_05_12 - Interagency Operations Advisory ...
OLSG Report_Final_06_05_12 - Interagency Operations Advisory ...
OLSG Report_Final_06_05_12 - Interagency Operations Advisory ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Optical Link Study Group (<strong>OLSG</strong>) <strong>Final</strong> <strong>Report</strong><br />
IOAG.T.<strong>OLSG</strong>.20<strong>12</strong>.V1<br />
• The data rate is 10 Gb/s.<br />
• Data are transmitted only above 20° elevation.<br />
• An example set of nine globally located ground terminals may provide optical<br />
communications to the satellite<br />
From these assumptions we deduce:<br />
• The average amount of data dumped per contact is 3 Tbit (= 5 min x 10 Gb/s).<br />
• With 15 orbits/day, the satellite shall dump, on average, 800 Gbit per orbit (= [<strong>12</strong><br />
Tbit/day]/[15 orbits/day]) with a high probability. Thus, 80s (= [800 Gb/orbit]/[10<br />
Gb/s]) of contact time per orbit is required.<br />
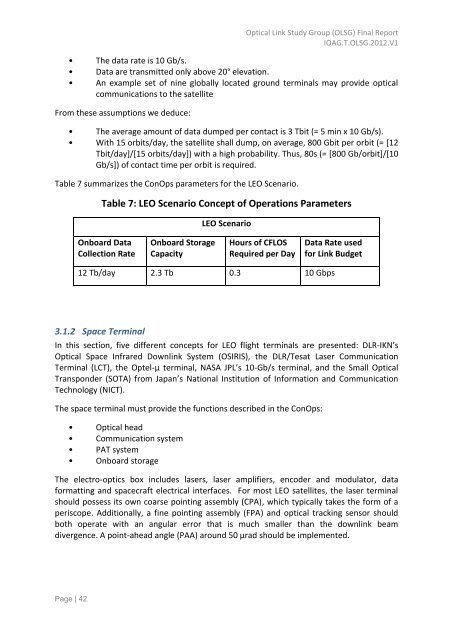
Table 7 summarizes the ConOps parameters for the LEO Scenario.<br />
Table 7: LEO Scenario Concept of <strong>Operations</strong> Parameters<br />
LEO Scenario<br />
Onboard Data<br />
Collection Rate<br />
Onboard Storage<br />
Capacity<br />
Hours of CFLOS<br />
Required per Day<br />
Data Rate used<br />
for Link Budget<br />
<strong>12</strong> Tb/day 2.3 Tb 0.3 10 Gbps<br />
3.1.2 Space Terminal<br />
In this section, five different concepts for LEO flight terminals are presented: DLR-IKN’s<br />
Optical Space Infrared Downlink System (OSIRIS), the DLR/Tesat Laser Communication<br />
Terminal (LCT), the Optel-µ terminal, NASA JPL’s 10-Gb/s terminal, and the Small Optical<br />
Transponder (SOTA) from Japan’s National Institution of Information and Communication<br />
Technology (NICT).<br />
The space terminal must provide the functions described in the ConOps:<br />
• Optical head<br />
• Communication system<br />
• PAT system<br />
• Onboard storage<br />
The electro-optics box includes lasers, laser amplifiers, encoder and modulator, data<br />
formatting and spacecraft electrical interfaces. For most LEO satellites, the laser terminal<br />
should possess its own coarse pointing assembly (CPA), which typically takes the form of a<br />
periscope. Additionally, a fine pointing assembly (FPA) and optical tracking sensor should<br />
both operate with an angular error that is much smaller than the downlink beam<br />
divergence. A point-ahead angle (PAA) around 50 µrad should be implemented.<br />
Page | 42