2013-2014 Math Grade 7.pdf
2013-2014 Math Grade 7.pdf
2013-2014 Math Grade 7.pdf
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
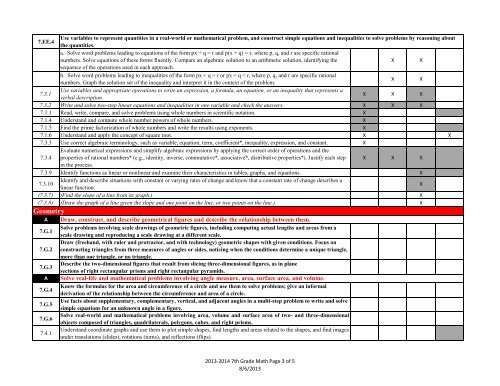
7.EE.4<br />
Use variables to represent quantities in a real-world or mathematical problem, and construct simple equations and inequalities to solve problems by reasoning about<br />
the quantities.<br />
a. Solve word problems leading to equations of the form px + q = r and p(x + q) = r, where p, q, and r are specific rational<br />
numbers. Solve equations of these forms fluently. Compare an algebraic solution to an arithmetic solution, identifying the<br />
X X<br />
sequence of the operations used in each approach.<br />
b. Solve word problems leading to inequalities of the form px + q > r or px + q < r, where p, q, and r are specific rational<br />
numbers. Graph the solution set of the inequality and interpret it in the context of the problem.<br />
X X<br />
7.3.1<br />
Use variables and appropriate operations to write an expression, a formula, an equation, or an inequality that represents a<br />
verbal description.<br />
X X X<br />
7.3.2 Write and solve two-step linear equations and inequalities in one variable and check the answers. X X X<br />
7.1.1 Read, write, compare, and solve problems using whole numbers in scientific notation. X<br />
7.1.4 Understand and compute whole number powers of whole numbers. X<br />
7.1.5 Find the prime factorization of whole numbers and write the results using exponents. X<br />
7.1.6 Understand and apply the concept of square root. X X<br />
7.3.3 Use correct algebraic terminology, such as variable, equation, term, coefficient*, inequality, expression, and constant. X<br />
Evaluate numerical expressions and simplify algebraic expressions by applying the correct order of operations and the<br />
7.3.4 properties of rational numbers* (e.g., identity, inverse, commutative*, associative*, distributive properties*). Justify each step X X X<br />
in the process.<br />
7.3.9 Identify functions as linear or nonlinear and examine their characteristics in tables, graphs, and equations. X<br />
7.3.10<br />
Identify and describe situations with constant or varying rates of change and know that a constant rate of change describes a<br />
linear function.<br />
X<br />
(7.3.7) (Find the slope of a line from its graph.) X<br />
(7.3.8) (Draw the graph of a line given the slope and one point on the line, or two points on the line.) X<br />
Geometry<br />
A<br />
7.G.1<br />
7.G.2<br />
7.G.3<br />
A<br />
7.G.4<br />
7.G.5<br />
7.G.6<br />
7.4.1<br />
Draw, construct, and describe geometrical figures and describe the relationship between them.<br />
Solve problems involving scale drawings of geometric figures, including computing actual lengths and areas from a<br />
scale drawing and reproducing a scale drawing at a different scale.<br />
Draw (freehand, with ruler and protractor, and with technology) geometric shapes with given conditions. Focus on<br />
constructing triangles from three measures of angles or sides, noticing when the conditions determine a unique triangle,<br />
more than one triangle, or no triangle.<br />
Describe the two-dimensional figures that result from slicing three-dimensional figures, as in plane<br />
sections of right rectangular prisms and right rectangular pyramids.<br />
Solve real-life and mathematical problems involving angle measure, area, surface area, and volume.<br />
Know the formulas for the area and circumference of a circle and use them to solve problems; give an informal<br />
derivation of the relationship between the circumference and area of a circle.<br />
Use facts about supplementary, complementary, vertical, and adjacent angles in a multi-step problem to write and solve<br />
simple equations for an unknown angle in a figure.<br />
Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving area, volume and surface area of two- and three-dimensional<br />
objects composed of triangles, quadrilaterals, polygons, cubes, and right prisms.<br />
Understand coordinate graphs and use them to plot simple shapes, find lengths and areas related to the shapes, and find images<br />
under translations (slides), rotations (turns), and reflections (flips).<br />
<strong>2013</strong>-<strong>2014</strong> 7th <strong>Grade</strong> <strong>Math</strong> Page 3 of 5<br />
8/6/<strong>2013</strong>