Palliative care for older people - World Health Organization ...
Palliative care for older people - World Health Organization ...
Palliative care for older people - World Health Organization ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
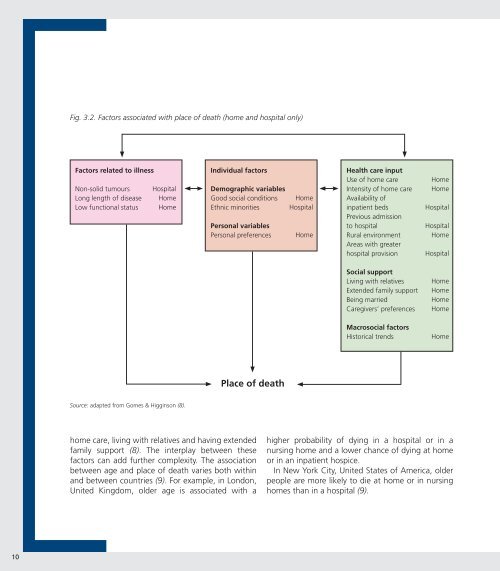
Fig. 3.2. Factors associated with place of death (home and hospital only)Factors related to illnessNon-solid tumoursLong length of diseaseLow functional statusHospitalHomeHomeIndividual factorsDemographic variablesGood social conditionsEthnic minoritiesPersonal variablesPersonal preferencesHomeHospitalHome<strong>Health</strong> <strong>care</strong> inputUse of home <strong>care</strong>Intensity of home <strong>care</strong>Availability ofinpatient bedsPrevious admissionto hospitalRural environmentAreas with greaterhospital provisionHomeHomeHospitalHospitalHomeHospitalSocial supportLiving with relativesExtended family supportBeing marriedCaregivers’ preferencesHomeHomeHomeHomeMacrosocial factorsHistorical trendsHomePlace of deathSource: adapted from Gomes & Higginson (8).home <strong>care</strong>, living with relatives and having extendedfamily support (8). The interplay between thesefactors can add further complexity. The associationbetween age and place of death varies both withinand between countries (9). For example, in London,United Kingdom, <strong>older</strong> age is associated with ahigher probability of dying in a hospital or in anursing home and a lower chance of dying at homeor in an inpatient hospice.In New York City, United States of America, <strong>older</strong><strong>people</strong> are more likely to die at home or in nursinghomes than in a hospital (9).10