Management of Snakebite and Research Management of Snakebite ...
Management of Snakebite and Research Management of Snakebite ...
Management of Snakebite and Research Management of Snakebite ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
PATIENTS AND METHODS<br />
Proven Russell’s viper bite patients with disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) entered<br />
into the study. Russell’s Viper envenomation was confirmed by identification <strong>of</strong> the dead<br />
snake <strong>and</strong>/or detection <strong>of</strong> specific venom antigen in serum by EIA (Khin-Ohn-Lwin et al.,<br />
1984, Tun-Pe et al., 1991). Patients under 12 <strong>and</strong> over 60 years <strong>and</strong> pregnant <strong>and</strong> lactating<br />
mothers were not included in the study. Patients were r<strong>and</strong>omly allocated to one <strong>of</strong> the<br />
following two treatment regimens:<br />
Regimen 1<br />
A single dose <strong>of</strong> 40 ml <strong>of</strong> ASV was given intravenously (IV) over 10 minutes. In those<br />
patients whose blood remained incoagulable six hours after the initial dose, another dose<br />
<strong>of</strong> 40 ml was given (IV over 10 minutes).<br />
Regimen 2<br />
A bolus dose <strong>of</strong> 80 ml <strong>of</strong> ASV (IV over 20 minutes). Lyophilized monovalent enzyme<br />
refined monospecific antivenom for Russell’s viper was used. Each individual patient was<br />
allocated to one <strong>of</strong> the above two regimens by lot.<br />
Analysis<br />
The two groups <strong>of</strong> patients were compared with respect to the patient’s characteristics,<br />
clinical features, progress, response <strong>and</strong> outcome. The patients under regimen one were<br />
carefully analysed to bring out the significant differences between those who needed 40<br />
ml only <strong>and</strong> those who required additional 40 ml. Statistical analysis was done by using<br />
student ‘’t’’ test (paired) <strong>and</strong> Chi square test.<br />
RESULTS<br />
Comparing regimens one <strong>and</strong> two<br />
A total <strong>of</strong> 45 patients were studied. 23 <strong>of</strong> them received regimen one <strong>and</strong> 22 patients<br />
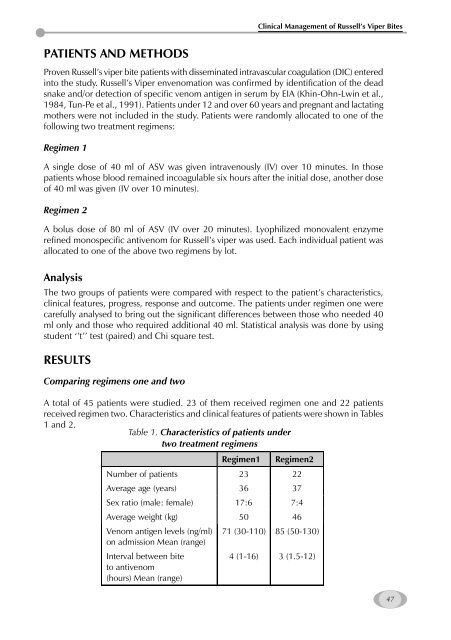
received regimen two. Characteristics <strong>and</strong> clinical features <strong>of</strong> patients were shown in Tables<br />
1 <strong>and</strong> 2.<br />
Table 1. Characteristics <strong>of</strong> patients under<br />
two treatment regimens<br />
Regimen1 Regimen2<br />
Number <strong>of</strong> patients 23 22<br />
Average age (years) 36 37<br />
Sex ratio (male: female) 17:6 7:4<br />
Average weight (kg) 50 46<br />
Venom antigen levels (ng/ml)<br />
on admission Mean (range)<br />
71 (30-110) 85 (50-130)<br />
Interval between bite<br />
to antivenom<br />
(hours) Mean (range)<br />
Clinical <strong>Management</strong> <strong>of</strong> Russell’s Viper Bites<br />
4 (1-16) 3 (1.5-12)<br />
47