MicroTCA TM - PICMG
MicroTCA TM - PICMG
MicroTCA TM - PICMG
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Not Intended for Design - Do not Claim Compliance<br />
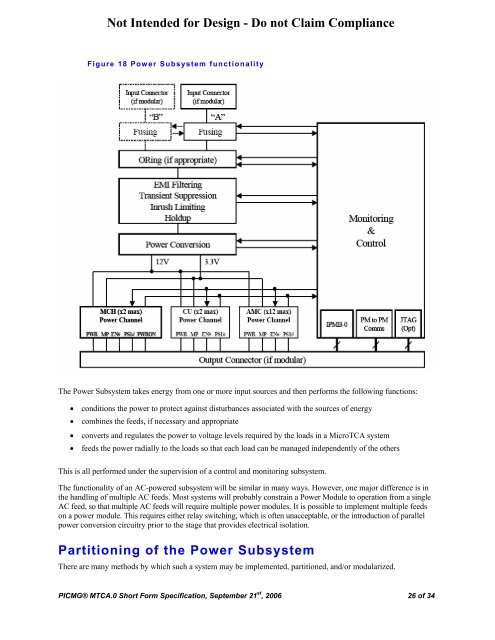
Figure 18 Power Subsystem functionality<br />
The Power Subsystem takes energy from one or more input sources and then performs the following functions:<br />
• conditions the power to protect against disturbances associated with the sources of energy<br />
• combines the feeds, if necessary and appropriate<br />
• converts and regulates the power to voltage levels required by the loads in a <strong>MicroTCA</strong> system<br />
• feeds the power radially to the loads so that each load can be managed independently of the others<br />
This is all performed under the supervision of a control and monitoring subsystem.<br />
The functionality of an AC-powered subsystem will be similar in many ways. However, one major difference is in<br />
the handling of multiple AC feeds. Most systems will probably constrain a Power Module to operation from a single<br />
AC feed, so that multiple AC feeds will require multiple power modules. It is possible to implement multiple feeds<br />
on a power module. This requires either relay switching, which is often unacceptable, or the introduction of parallel<br />
power conversion circuitry prior to the stage that provides electrical isolation.<br />
Partitioning of the Power Subsystem<br />
There are many methods by which such a system may be implemented, partitioned, and/or modularized.<br />
<strong>PICMG</strong>® MTCA.0 Short Form Specification, September 21 st , 2006 26 of 34