Chapter 1 Gas Power Cycle
Chapter 1 Gas Power Cycle
Chapter 1 Gas Power Cycle
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
(b) w net = q H –q L , similar to q 23 ; -q L =q 41 = u 1 –u 4<br />
3-4 Isentropic proc.<br />
v r4/v r3 = v 4/v 3 , v 4/v 3 =r v = 8, � v r4 = v r3r v = 6.108*8.0 = 48.864<br />
Table A-17 : at v r4 = 48.864 � T 2 = 795.6 K and u 4 =588.74 kJ/kg,<br />
4-1 Constant volume heat rejected,<br />
1 st law q 41 = w 41 + u 1 –u 4 ; w 41 = 0<br />
q 41 = u 1 –u 4 = 206.91 - 588.74 = -381.83 kJ/kg<br />
q L = -q 41 = 381.83 kJ/kg<br />
w net = q H –q L = 800 – 381.83 = 418.17 kJ/kg answer<br />
(c) η th = w net /q H = 418.83/800 = 0.523 or 52.3 % answer<br />
(d) MEP = w net /(v 1-v 2 ) ; P 1v 1 = RT 1<br />
� v 1 = 0.832 m 3 /kg , v 2 =v 1/8,<br />
MEP = 574.4 kPa answer<br />
Spark-ignition Engine<br />
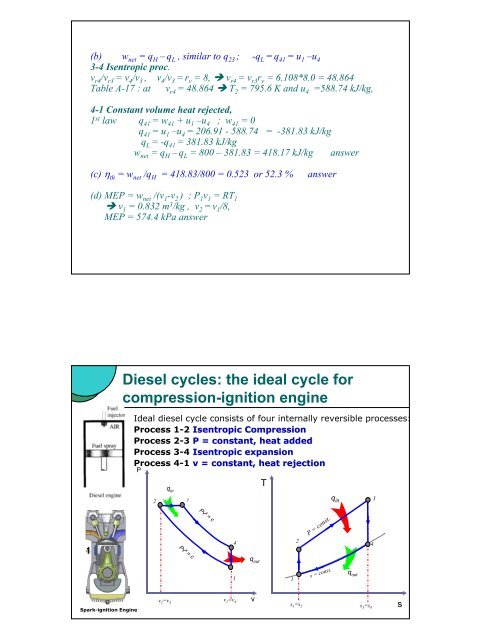
Diesel cycles: the ideal cycle for<br />
compression-ignition engine<br />
Ideal diesel cycle consists of four internally reversible processes:<br />
Process 1-2 Isentropic Compression<br />
Process 2-3 P = constant, heat added<br />
Process 3-4 Isentropic expansion<br />
Process 4-1 v = constant, heat rejection<br />
P<br />
2<br />
q in<br />
v 2 =v 3<br />
3<br />
Pv k = c<br />
Pv k = c<br />
4<br />
1<br />
v 1 =v 4<br />
q out<br />
v<br />
T<br />
1<br />
2<br />
P = const.<br />
v = const.<br />
q in<br />
q out<br />
s 1 =s 2 s3 =s 4<br />
4<br />
3<br />
s