Measuring Gas Velocity with the D-FL 100 Differential Pressure Bar
Measuring Gas Velocity with the D-FL 100 Differential Pressure Bar
Measuring Gas Velocity with the D-FL 100 Differential Pressure Bar
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
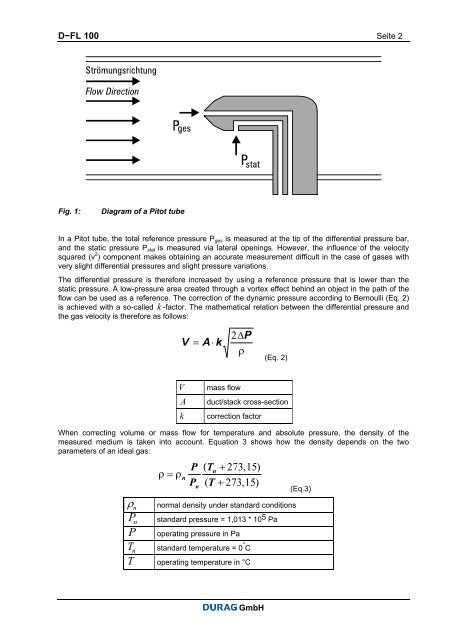
D−<strong>FL</strong> <strong>100</strong> Seite 2Fig. 1:Diagram of a Pitot tubeIn a Pitot tube, <strong>the</strong> total reference pressure P ges is measured at <strong>the</strong> tip of <strong>the</strong> differential pressure bar,and <strong>the</strong> static pressure P stat is measured via lateral openings. However, <strong>the</strong> influence of <strong>the</strong> velocitysquared (v 2 ) component makes obtaining an accurate measurement difficult in <strong>the</strong> case of gases <strong>with</strong>very slight differential pressures and slight pressure variations.The differential pressure is <strong>the</strong>refore increased by using a reference pressure that is lower than <strong>the</strong>static pressure. A low-pressure area created through a vortex effect behind an object in <strong>the</strong> path of <strong>the</strong>flow can be used as a reference. The correction of <strong>the</strong> dynamic pressure according to Bernoulli (Eq. 2)is achieved <strong>with</strong> a so-called k -factor. The ma<strong>the</strong>matical relation between <strong>the</strong> differential pressure and<strong>the</strong> gas velocity is <strong>the</strong>refore as follows:(Eq. 2)VAkmass flowduct/stack cross-sectioncorrection factorWhen correcting volume or mass flow for temperature and absolute pressure, <strong>the</strong> density of <strong>the</strong>measured medium is taken into account. Equation 3 shows how <strong>the</strong> density depends on <strong>the</strong> twoparameters of an ideal gas:(Eq.3)ρ n normal density under standard conditionsP n standard pressure = 1,013 * 10 5 PaP operating pressure in PaT n standard temperature = 0 ° CT operating temperature in °CGmbH