Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Algorithm - NHS Cumbria
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Algorithm - NHS Cumbria
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Algorithm - NHS Cumbria
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
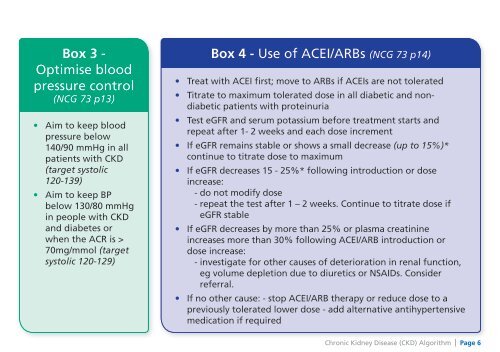
Box 3 -Optimise bloodpressure control(NCG 73 p13)• Aim to keep bloodpressure below140/90 mmHg in allpatients with <strong>CKD</strong>(target systolic120-139)• Aim to keep BPbelow 130/80 mmHgin people with <strong>CKD</strong>and diabetes orwhen the ACR is >70mg/mmol (targetsystolic 120-129)Box 4 - Use of ACEI/ARBs (NCG 73 p14)• Treat with ACEI first; move to ARBs if ACEIs are not tolerated• Titrate to maximum tolerated dose in all diabetic and nondiabeticpatients with proteinuria• Test eGFR and serum potassium before treatment starts andrepeat after 1- 2 weeks and each dose increment• If eGFR remains stable or shows a small decrease (up to 15%)*continue to titrate dose to maximum• If eGFR decreases 15 - 25%* following introduction or doseincrease:- do not modify dose- repeat the test after 1 – 2 weeks. Continue to titrate dose ifeGFR stable• If eGFR decreases by more than 25% or plasma creatinineincreases more than 30% following ACEI/ARB introduction ordose increase:- investigate for other causes of deterioration in renal function,eg volume depletion due to diuretics or NSAIDs. Considerreferral.• If no other cause: - stop ACEI/ARB therapy or reduce dose to apreviously tolerated lower dose - add alternative antihypertensivemedication if required<strong>Chronic</strong> <strong>Kidney</strong> <strong>Disease</strong> (<strong>CKD</strong>) <strong>Algorithm</strong> | Page 6