Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Algorithm - NHS Cumbria
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Algorithm - NHS Cumbria
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Algorithm - NHS Cumbria
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
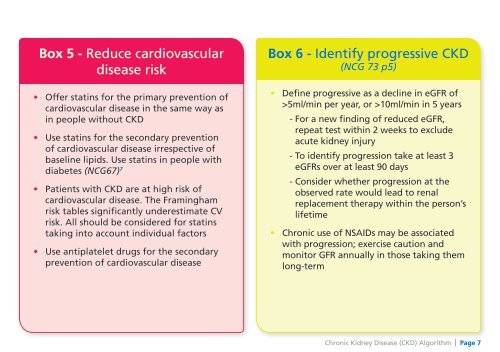
Box 5 - Reduce cardiovasculardisease risk• Offer statins for the primary prevention ofcardiovascular disease in the same way asin people without <strong>CKD</strong>• Use statins for the secondary preventionof cardiovascular disease irrespective ofbaseline lipids. Use statins in people withdiabetes (NCG67) 7• Patients with <strong>CKD</strong> are at high risk ofcardiovascular disease. The Framinghamrisk tables significantly underestimate CVrisk. All should be considered for statinstaking into account individual factors• Use antiplatelet drugs for the secondaryprevention of cardiovascular diseaseBox 6 - Identify progressive <strong>CKD</strong>(NCG 73 p5)• Define progressive as a decline in eGFR of>5ml/min per year, or >10ml/min in 5 years- For a new finding of reduced eGFR,repeat test within 2 weeks to excludeacute kidney injury- To identify progression take at least 3eGFRs over at least 90 days- Consider whether progression at theobserved rate would lead to renalreplacement therapy within the person’slifetime• <strong>Chronic</strong> use of NSAIDs may be associatedwith progression; exercise caution andmonitor GFR annually in those taking themlong-term<strong>Chronic</strong> <strong>Kidney</strong> <strong>Disease</strong> (<strong>CKD</strong>) <strong>Algorithm</strong> | Page 7