Literature Review - HSC Home - University of the West of England
Literature Review - HSC Home - University of the West of England
Literature Review - HSC Home - University of the West of England
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
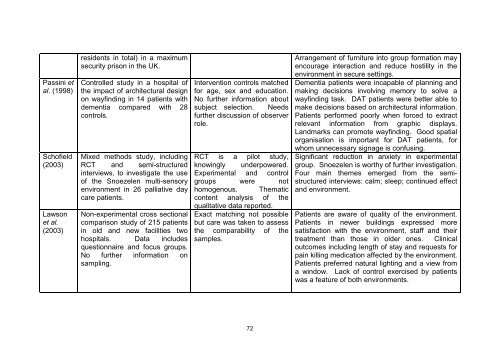
Passini etal. (1998)Sch<strong>of</strong>ield(2003)Lawsonet al.(2003)residents in total) in a maximumsecurity prison in <strong>the</strong> UK.Controlled study in a hospital <strong>of</strong><strong>the</strong> impact <strong>of</strong> architectural designon wayfinding in 14 patients withdementia compared with 28controls.Mixed methods study, includingRCT and semi-structuredinterviews, to investigate <strong>the</strong> use<strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> Snoezelen multi-sensoryenvironment in 26 palliative daycare patients.Non-experimental cross sectionalcomparison study <strong>of</strong> 215 patientsin old and new facilities twohospitals. Data includesquestionnaire and focus groups.No fur<strong>the</strong>r information onsampling.Intervention controls matchedfor age, sex and education.No fur<strong>the</strong>r information aboutsubject selection. Needsfur<strong>the</strong>r discussion <strong>of</strong> observerrole.RCT is a pilot study,knowingly underpowered.Experimental and controlgroups were nothomogenous. Thematiccontent analysis <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong>qualitative data reported.Exact matching not possiblebut care was taken to assess<strong>the</strong> comparability <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong>samples.Arrangement <strong>of</strong> furniture into group formation mayencourage interaction and reduce hostility in <strong>the</strong>environment in secure settings.Dementia patients were incapable <strong>of</strong> planning andmaking decisions involving memory to solve awayfinding task. DAT patients were better able tomake decisions based on architectural information.Patients performed poorly when forced to extractrelevant information from graphic displays.Landmarks can promote wayfinding. Good spatialorganisation is important for DAT patients, forwhom unnecessary signage is confusing.Significant reduction in anxiety in experimentalgroup. Snoezelen is worthy <strong>of</strong> fur<strong>the</strong>r investigation.Four main <strong>the</strong>mes emerged from <strong>the</strong> semistructuredinterviews: calm; sleep; continued effectand environment.Patients are aware <strong>of</strong> quality <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> environment.Patients in newer buildings expressed moresatisfaction with <strong>the</strong> environment, staff and <strong>the</strong>irtreatment than those in older ones. Clinicaloutcomes including length <strong>of</strong> stay and requests forpain killing medication affected by <strong>the</strong> environment.Patients preferred natural lighting and a view froma window. Lack <strong>of</strong> control exercised by patientswas a feature <strong>of</strong> both environments.72