The Adoption of Agricultural Technology - Food Security Group
The Adoption of Agricultural Technology - Food Security Group
The Adoption of Agricultural Technology - Food Security Group
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
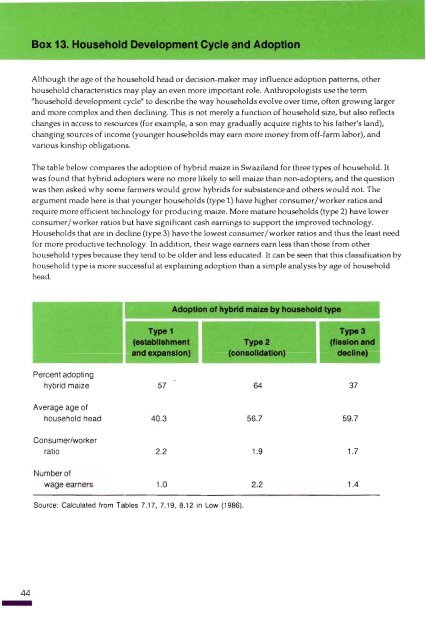
Box 13. Household Development Cycle and <strong>Adoption</strong>Although the age <strong>of</strong> the household head or decision-maker may influence adoption patterns, otherhousehold characteristics may play an even more important role. Anthropologists use the term"household development cycle" to describe the way households evolve over time, <strong>of</strong>ten growing largerand more complex and then declining. This is not merely a function <strong>of</strong> household size, but also reflectschanges in access to resources (for example, a son may gradually acquire rights to his father's land),changing sources <strong>of</strong> income (younger households may earn more money from <strong>of</strong>f-farm labor), andvarious kinship obligations.<strong>The</strong> table below compares the adoption <strong>of</strong> hybrid maize in Swaziland for three types <strong>of</strong> household. Itwas found that hybrid adopters were no more likely to sell maize than non-adopters, and the questionwas then asked why some farmers would grow hybrids for subsistence and others would not. <strong>The</strong>argument made here is that younger households (type 1) have higher consumer/worker ratios andrequire more efficient technology for producing maize. More mature households (type 2) have lowerconsumer/ worker ratios but have significant cash earnings to support the improved technology.Households that are in decline (type 3) have the lowest consumer/worker ratios and thus the least needfor more productive technology. In addition, their wage earners earn less than those from otherhousehold types because they tend to be older and less educated. It can be seen that this classification byhousehold type is more successful at explaining adoption than a simple analysis by age <strong>of</strong> householdhead.<strong>Adoption</strong> <strong>of</strong> hybrid maize by household type.......Type 1 Type 3(establishment Type 2 (fission andand expansion) (consolidation) decline)Percent adoptinghybrid maize 57 64 37Average age <strong>of</strong>household head 40.3 56.7 59.7Consumer/workerratio 2.2 1.9 1.7Number <strong>of</strong>wage earners 1.0 2.21.4Source: Calculated from Tables 7.17, 7.19, 8.12 in Low (1986).44