Wetlands in northern Salt Lake Valley, Salt Lake County, Utah
Wetlands in northern Salt Lake Valley, Salt Lake County, Utah
Wetlands in northern Salt Lake Valley, Salt Lake County, Utah
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
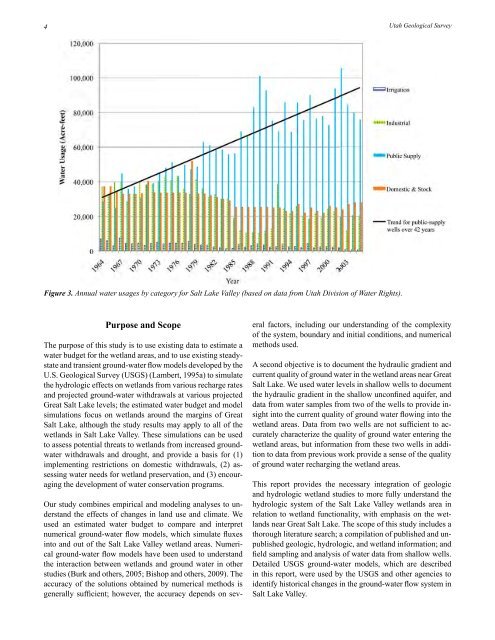
4<strong>Utah</strong> Geological SurveyFigure 3. Annual water usages by category for <strong>Salt</strong> <strong>Lake</strong> <strong>Valley</strong> (based on data from <strong>Utah</strong> Division of Water Rights).Purpose and ScopeThe purpose of this study is to use exist<strong>in</strong>g data to estimate awater budget for the wetland areas, and to use exist<strong>in</strong>g steadystateand transient ground-water flow models developed by theU.S. Geological Survey (USGS) (Lambert, 1995a) to simulatethe hydrologic effects on wetlands from various recharge ratesand projected ground-water withdrawals at various projectedGreat <strong>Salt</strong> <strong>Lake</strong> levels; the estimated water budget and modelsimulations focus on wetlands around the marg<strong>in</strong>s of Great<strong>Salt</strong> <strong>Lake</strong>, although the study results may apply to all of thewetlands <strong>in</strong> <strong>Salt</strong> <strong>Lake</strong> <strong>Valley</strong>. These simulations can be usedto assess potential threats to wetlands from <strong>in</strong>creased groundwaterwithdrawals and drought, and provide a basis for (1)implement<strong>in</strong>g restrictions on domestic withdrawals, (2) assess<strong>in</strong>gwater needs for wetland preservation, and (3) encourag<strong>in</strong>gthe development of water conservation programs.Our study comb<strong>in</strong>es empirical and model<strong>in</strong>g analyses to understandthe effects of changes <strong>in</strong> land use and climate. Weused an estimated water budget to compare and <strong>in</strong>terpretnumerical ground-water flow models, which simulate fluxes<strong>in</strong>to and out of the <strong>Salt</strong> <strong>Lake</strong> <strong>Valley</strong> wetland areas. Numericalground-water flow models have been used to understandthe <strong>in</strong>teraction between wetlands and ground water <strong>in</strong> otherstudies (Burk and others, 2005; Bishop and others, 2009). Theaccuracy of the solutions obta<strong>in</strong>ed by numerical methods isgenerally sufficient; however, the accuracy depends on severalfactors, <strong>in</strong>clud<strong>in</strong>g our understand<strong>in</strong>g of the complexityof the system, boundary and <strong>in</strong>itial conditions, and numericalmethods used.A second objective is to document the hydraulic gradient andcurrent quality of ground water <strong>in</strong> the wetland areas near Great<strong>Salt</strong> <strong>Lake</strong>. We used water levels <strong>in</strong> shallow wells to documentthe hydraulic gradient <strong>in</strong> the shallow unconf<strong>in</strong>ed aquifer, anddata from water samples from two of the wells to provide <strong>in</strong>sight<strong>in</strong>to the current quality of ground water flow<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>to thewetland areas. Data from two wells are not sufficient to accuratelycharacterize the quality of ground water enter<strong>in</strong>g thewetland areas, but <strong>in</strong>formation from these two wells <strong>in</strong> additionto data from previous work provide a sense of the qualityof ground water recharg<strong>in</strong>g the wetland areas.This report provides the necessary <strong>in</strong>tegration of geologicand hydrologic wetland studies to more fully understand thehydrologic system of the <strong>Salt</strong> <strong>Lake</strong> <strong>Valley</strong> wetlands area <strong>in</strong>relation to wetland functionality, with emphasis on the wetlandsnear Great <strong>Salt</strong> <strong>Lake</strong>. The scope of this study <strong>in</strong>cludes athorough literature search; a compilation of published and unpublishedgeologic, hydrologic, and wetland <strong>in</strong>formation; andfield sampl<strong>in</strong>g and analysis of water data from shallow wells.Detailed USGS ground-water models, which are described<strong>in</strong> this report, were used by the USGS and other agencies toidentify historical changes <strong>in</strong> the ground-water flow system <strong>in</strong><strong>Salt</strong> <strong>Lake</strong> <strong>Valley</strong>.