ARTES-5.1 â ESA Telecom Technology Workplan ... - Emits - ESA
ARTES-5.1 â ESA Telecom Technology Workplan ... - Emits - ESA
ARTES-5.1 â ESA Telecom Technology Workplan ... - Emits - ESA
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
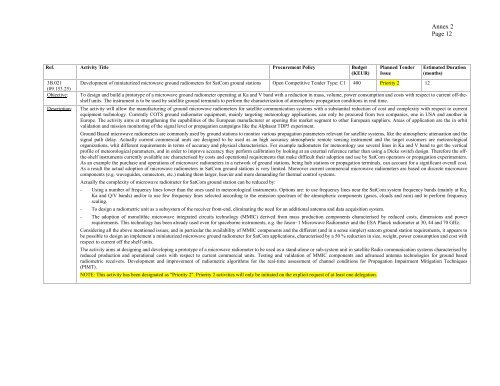
Annex 2Page 12Ref. Activity Title Procurement Policy Budget(KEUR)3B.021(09.153.25)Objective:Description:Planned TenderIssueDevelopment of miniaturized microwave ground radiometers for SatCom ground stations Open Competitive Tender Type: C1 400 Priority 2 12Estimated Duration(months)To design and build a prototype of a microwave ground radiometer operating at Ka and V band with a reduction in mass, volume, power consumption and costs with respect to current off-theshelfunits. The instrument is to be used by satellite ground terminals to perform the characterization of atmospheric propagation conditions in real time.The activity will allow the manufacturing of ground microwave radiometers for satellite communication systems with a substantial reduction of cost and complexity with respect to currentequipment technology. Currently COTS ground radiometer equipment, mainly targeting meteorology applications, can only be procured from two companies, one in USA and another inEurope. The activity aims at strengthening the capabilities of the European manufacturer or opening this market segment to other European suppliers. Areas of application are the in orbitvalidation and mission monitoring of the signal level or propagation campaigns like the Alphasat TDP5 experiment.Ground Based microwave radiometers are commonly used by ground stations to monitor various propagation parameters relevant for satellite systems, like the atmospheric attenuation and thesignal path delay. Actually current commercial units are designed to be used as an high accuracy atmospheric remote sensing instrument and the target customers are meteorologicalorganizations, whit different requirements in terms of accuracy and physical characteristics. For example radiometers for meteorology use several lines in Ka and V band to get the verticalprofile of meteorological parameters, and in order to improve accuracy they perform calibration by looking at an external reference rather than using a Dicke switch design. Therefore the offthe-shelfinstruments currently available are characterised by costs and operational requirements that make difficult their adoption and use by SatCom operators or propagation experimenters.As an example the purchase and operations of microwave radiometers in a network of ground stations, being hub stations or propagation terminals, can account for a significant overall cost.As a result the actual adoption of microwave radiometers in SatCom ground stations is very limited. Moreover current commercial microwave radiometers are based on discrete microwavecomponents (e.g. waveguides, connectors, etc.) making them larger, heavier and more demanding for thermal control systems.Actually the complexity of microwave radiometer for SatCom ground station can be reduced by:- Using a number of frequency lines lower than the ones used in meteorological instruments. Options are: to use frequency lines near the SatCom system frequency bands (mainly at Ku,Ka and Q/V bands) and/or to use few frequency lines selected according to the emission spectrum of the atmospheric components (gases, clouds and rain) and to perform frequencyscaling.- To design a radiometric unit as a subsystem of the receiver front-end, eliminating the need for an additional antenna and data acquisition system.- The adoption of monolithic microwave integrated circuits technology (MMIC) derived from mass production components characterised by reduced costs, dimensions and powerrequirements. This technology has been already used even for spaceborne instruments, e.g. the Jason−1 Microwave Radiometer and the <strong>ESA</strong> Planck radiometer at 30, 44 and 70 GHz.Considering all the above mentioned issues, and in particular the availability of MMIC components and the different (and in a sense simpler) satcom ground station requirements, it appears tobe possible to design an implement a miniaturized microwave ground radiometer for SatCom applications, characterised by a 50 % reduction in size, weight, power consumption and cost withrespect to current off the shelf units.The activity aims at designing and developing a prototype of a microwave radiometer to be used as a stand-alone or sub-system unit in satellite Radio communication systems characterised byreduced production and operational costs with respect to current commercial units. Testing and validation of MMIC components and advanced antenna technologies for ground basedradiometric receivers. Development and improvement of radiometric algorithms for the real-time assessment of channel conditions for Propagation Impairment Mitigation Techniques(PIMT).NOTE: This activity has been designated as "Priority 2". Priority 2 activities will only be initiated on the explicit request of at least one delegation.