- Page 2:
© 2002 by CRC Press LLCModeling To
- Page 5 and 6:
ContentsPrefaceAcknowledgmentsFUNDA
- Page 7 and 8:
APPLICATIONS8. MODELING OF ENGINEER
- Page 9 and 10:
The contents of this book are organ
- Page 11 and 12:
PART IFundamentals© 2002 by CRC Pr
- Page 13 and 14:
The models resulting from the model
- Page 15 and 16:
within the grasp of only a few with
- Page 17 and 18:
1.2.3 STATIC VS. DYNAMICWhen a syst
- Page 19 and 20:
Real SystemsMathematical ModelsDete
- Page 21 and 22:
through several pathways. Consequen
- Page 23 and 24:
ange of complex environmental appli
- Page 25 and 26:
APPENDIX 1.1 TYPICAL USES OF MATHEM
- Page 27 and 28:
APPENDIX 1.2 (continued)Target Audi
- Page 29 and 30:
characteristics. The system is isol
- Page 31 and 32:
formation, inferencing, testing, va
- Page 33 and 34:
system-surroundings interactions ca
- Page 35 and 36:
2.2.4 INTERPRETATION AND EVALUATION
- Page 37 and 38:
to fill in where scientific theorie
- Page 39 and 40:
Figure 2.3 Schematic of real system
- Page 41 and 42:
Table 2.1 Variables, Symbols, Dimen
- Page 43 and 44:
∴Net diffusive inflow = -EA ∂
- Page 45 and 46:
in terms of the model parameters al
- Page 47 and 48:
Figure 2.8 Model predictions vs. me
- Page 49 and 50:
variables. Deterministic systems ca
- Page 51 and 52:
e possible, and a computational met
- Page 53 and 54:
or, in matrix forma 11 a 12 a 13a 2
- Page 55 and 56:
(a)(b)Figure 3.3 (a) Setting up Sol
- Page 57 and 58:
Figure 3.5 Using MATLAB ® for solv
- Page 59 and 60:
Another method, known as the Newton
- Page 61 and 62:
and so on up tof n (x 1 , x 2 , . .
- Page 63 and 64:
c. Second-order equation with equid
- Page 65 and 66:
Figure 3.9 Solution of ODE by Mathe
- Page 67 and 68: over the entire step, which may be
- Page 69 and 70: Hence, the original problem is now
- Page 71 and 72: 2∂ f f i1,j1 - f i-1,j1 - f i1,j-
- Page 73 and 74: modeling, in diagnosis and troubles
- Page 75 and 76: For the reach x ≥ a: C S D K
- Page 77 and 78: contaminants that do not undergo an
- Page 79 and 80: known as an intensive property. Oth
- Page 81 and 82: Dissolved mass in sample = dissolve
- Page 83 and 84: Figure 4.2 Illustration of steady s
- Page 85 and 86: 4.3.2.2 Dalton’s LawDalton’s La
- Page 87 and 88: Table 4.2 Different Forms of Quanti
- Page 89 and 90: M olesoxygenHence, K a-w = = 8 - 3
- Page 91 and 92: SolutionThe flux, N, which is the d
- Page 93 and 94: Figure 4.3 Illustration of the Two-
- Page 95 and 96: where C s is the concentration of t
- Page 97 and 98: Fraction in dissolved form = f d =
- Page 99 and 100: in the air (M/L -3 ), C a is the co
- Page 101 and 102: ackward reactions can expressed in
- Page 103 and 104: 4.7.2 ELEMENTARY REACTIONSThe rate
- Page 105 and 106: excess energy. The direct photolysi
- Page 107 and 108: 4.8 MATERIAL BALANCEAs indicated in
- Page 109 and 110: SolutionLet M be the mass of chemic
- Page 111 and 112: CpHence, the final result isEXERCIS
- Page 113 and 114: APPENDIX 4.1 COMMON PARTITION COEFF
- Page 115 and 116: analyzing and modeling them. The ex
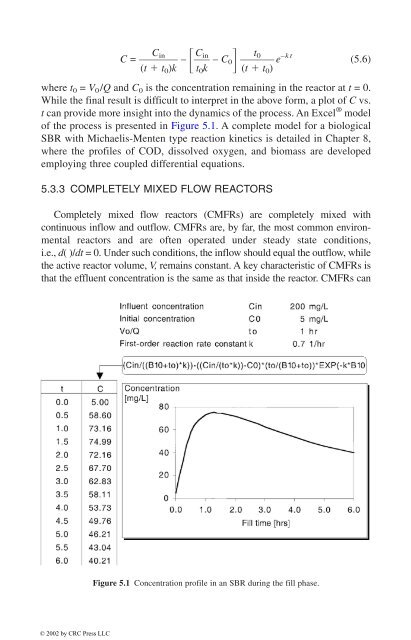
- Page 117: \5.2.2 HETEROGENEOUS REACTORSHetero
- Page 121 and 122: Worked Example 5.1A wastewater trea
- Page 123 and 124: or,C L = C 0 e -(k /u)L = C 0 e -k
- Page 125 and 126: HRT = 1 k (1 - )The overall HRT
- Page 127 and 128: The MB equation for the above syste
- Page 129 and 130: the particle surface (ML -2 T -1 ),
- Page 131 and 132: 0 = QX - Q(X - dX) - K L (aAdz)(X -
- Page 133 and 134: chemical engineering applications.
- Page 135 and 136: This expression does not provide an
- Page 137 and 138: If the WWTP used air instead of pur
- Page 139 and 140: and degradation of the natural envi
- Page 141 and 142: The solution to the above PDE gives
- Page 143 and 144: • river 2: x = 15000.5 dmay ∴u
- Page 145 and 146: These functions are valuable tools
- Page 147 and 148: this problem. Once the basic “syn
- Page 149 and 150: giving the condition Q > 4πRu for
- Page 151 and 152: directions, and the last term repre
- Page 153 and 154: SolutionTo be conservative, it may
- Page 155 and 156: zone, because the hydraulic conduct
- Page 157 and 158: 6.2.5 FLOW OF AIR AND CONTAMINANTS
- Page 159 and 160: time-dependent volumetric flow rate
- Page 161 and 162: Solution(1) The steady state concen
- Page 163 and 164: As a first step in modeling a river
- Page 165 and 166: where a 1,4 is the conversion facto
- Page 167 and 168: © 2002 by CRC Press LLCFigure 6.8
- Page 169 and 170:
Figure 6.106.5 Consider the stream
- Page 171 and 172:
Case 4: Pulse Source in Two Dimensi
- Page 173 and 174:
End users often adapted these model
- Page 175 and 176:
to further enhance the capabilities
- Page 177 and 178:
are always expressed in the standar
- Page 179 and 180:
know the program’s environment. M
- Page 181 and 182:
typing in the equations in algebrai
- Page 183 and 184:
accessed in Simulink ® models. The
- Page 185 and 186:
By combining the above simple funct
- Page 187 and 188:
Concentration [mg/L]Figure 7.3 Lake
- Page 189 and 190:
saving considerable model building
- Page 191 and 192:
dependent variable, the dependent v
- Page 193 and 194:
command is used to keep the plot fr
- Page 195 and 196:
Figure 7.10 Lake problem solved wit
- Page 197 and 198:
simulation. This enables, for examp
- Page 199 and 200:
Figure 7.13 Lake problem modeled in
- Page 201 and 202:
It is hoped that the above overview
- Page 203 and 204:
APPENDIX 7.2 EXAMPLES OF TYPES OF E
- Page 205 and 206:
CHAPTER 8Modeling of EngineeredEnvi
- Page 207 and 208:
MB on dissolved oxygen: dC od xyt=
- Page 209 and 210:
© 2002 by CRC Press LLCFigure 8.1
- Page 211 and 212:
Table 8.2 SBR Model Equations Gener
- Page 213 and 214:
Figure 8.4 Predicted vs. measured C
- Page 215 and 216:
mathematical model. First, a proces
- Page 217 and 218:
Figure 8.9 Pretreatment system—ef
- Page 219 and 220:
Figure 8.11 CMFRs in series: optimi
- Page 221 and 222:
Other improvements can include alte
- Page 223 and 224:
Figure 8.15 Model of wastewater tre
- Page 225 and 226:
8.5 MODELING EXAMPLE: CHEMICAL OXID
- Page 227 and 228:
When Mathematica ® cannot find ana
- Page 229 and 230:
Figure 8.20 Chemical oxidation proc
- Page 231 and 232:
Figure 8.22 Chemical oxidation proc
- Page 233 and 234:
Figure 8.24 Chemical oxidation proc
- Page 235 and 236:
fairly large and may not be suitabl
- Page 237 and 238:
© 2002 by CRC Press LLCFigure 8.27
- Page 239 and 240:
where q is the mass of color adsorb
- Page 241 and 242:
Figure 8.29 Results of activated ca
- Page 243 and 244:
and d X = (µ - b)Xdtwhere b is the
- Page 245 and 246:
Figure 8.32 Results of bioregenerat
- Page 247 and 248:
under a set of known data, the stat
- Page 249 and 250:
MB across element on oxygen in gas
- Page 251 and 252:
Figure 8.38 Typical results of oxyg
- Page 253 and 254:
Figure 8.39 Mathematica ® script f
- Page 255 and 256:
entered as a function of x and y, u
- Page 257 and 258:
To generalize the approach, the gov
- Page 259 and 260:
Figure 8.44 Concentration in pore g
- Page 261 and 262:
modeling of a sample problem from T
- Page 263 and 264:
Figure 9.2 Lakes in series modeled
- Page 265 and 266:
Figure 9.4 Two lakes in series mode
- Page 267 and 268:
In this example, a two-compartment
- Page 269 and 270:
in the sediments, v b is the burial
- Page 271 and 272:
Figure 9.9 Algal growth modeled in
- Page 273 and 274:
Figure 9.11 Algal growth modeled in
- Page 275 and 276:
Once the basic model is constructed
- Page 277 and 278:
Figure 9.15 Graphical user interfac
- Page 279 and 280:
Figure 9.17 Contaminant transport v
- Page 281 and 282:
Figure 9.19 Contaminant transport v
- Page 283 and 284:
© 2002 by CRC Press LLCFigure 9.20
- Page 285 and 286:
Figure 9.21 Chemical equilibrium mo
- Page 287 and 288:
MB on liver:MB on bones: d P2 = k 2
- Page 289 and 290:
Table 9.3 Model Equations in ithink
- Page 291 and 292:
Figure 9.25 Problem definition for
- Page 293 and 294:
Figure 9.28 Groundwater flow visual
- Page 295 and 296:
W and the second to V, in line 6. T
- Page 297 and 298:
Figure 9.30 Three-dimensional conto
- Page 299 and 300:
VerticalDispersion CoefficientsHori
- Page 301 and 302:
configuration of the unit world pro
- Page 303 and 304:
342Chemical Mass Distribution [%]11
- Page 305 and 306:
water quality standard of 500 mg/L
- Page 307 and 308:
Hence, Q π tan-1 - 1 - UL - 1Q/
- Page 309 and 310:
Figure 9.38d Stream lines and veloc
- Page 311 and 312:
BibliographyBedient P. B., Rifai, H
- Page 313:
Nirmalakhandan, N., Jang, W., and S