Shark -new motor design concept for energy saving- applied to - VBN
Shark -new motor design concept for energy saving- applied to - VBN
Shark -new motor design concept for energy saving- applied to - VBN
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
36<br />
Chapter 2 Linear analysis of the <strong>Shark</strong> switched Reluctance Mo<strong>to</strong>r<br />
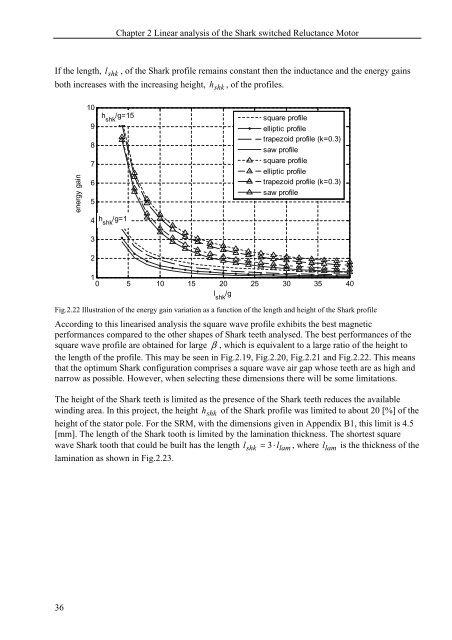
If the length, l shk , of the <strong>Shark</strong> profile remains constant then the inductance and the <strong>energy</strong> gains<br />
both increases with the increasing height, h shk , of the profiles.<br />
<strong>energy</strong> gain<br />
10<br />
9<br />
8<br />
7<br />
6<br />
5<br />
4<br />
3<br />
2<br />
h shk /g=15 square profile<br />
h shk /g=1<br />
elliptic profile<br />
trapezoid profile (k=0.3)<br />
saw profile<br />
square profile<br />
elliptic profile<br />
trapezoid profile (k=0.3)<br />
saw profile<br />
1<br />
0 5 10 15 20<br />
l /g<br />
shk<br />
25 30 35 40<br />
Fig.2.22 Illustration of the <strong>energy</strong> gain variation as a function of the length and height of the <strong>Shark</strong> profile<br />
According <strong>to</strong> this linearised analysis the square wave profile exhibits the best magnetic<br />
per<strong>for</strong>mances compared <strong>to</strong> the other shapes of <strong>Shark</strong> teeth analysed. The best per<strong>for</strong>mances of the<br />
square wave profile are obtained <strong>for</strong> large β , which is equivalent <strong>to</strong> a large ratio of the height <strong>to</strong><br />
the length of the profile. This may be seen in Fig.2.19, Fig.2.20, Fig.2.21 and Fig.2.22. This means<br />
that the optimum <strong>Shark</strong> configuration comprises a square wave air gap whose teeth are as high and<br />
narrow as possible. However, when selecting these dimensions there will be some limitations.<br />
The height of the <strong>Shark</strong> teeth is limited as the presence of the <strong>Shark</strong> teeth reduces the available<br />
winding area. In this project, the height h shk of the <strong>Shark</strong> profile was limited <strong>to</strong> about 20 [%] of the<br />
height of the sta<strong>to</strong>r pole. For the SRM, with the dimensions given in Appendix B1, this limit is 4.5<br />
[mm]. The length of the <strong>Shark</strong> <strong>to</strong>oth is limited by the lamination thickness. The shortest square<br />
wave <strong>Shark</strong> <strong>to</strong>oth that could be built has the length lshk = 3 ⋅ llam<br />
, where l lam is the thickness of the<br />
lamination as shown in Fig.2.23.