How Cells make ATP: Energy-Releasing Pathways - University City ...
How Cells make ATP: Energy-Releasing Pathways - University City ...
How Cells make ATP: Energy-Releasing Pathways - University City ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
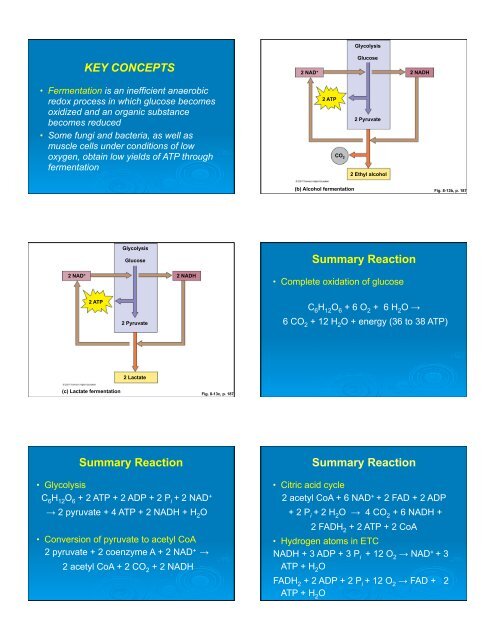
GlycolysisKEY CONCEPTSGlucose2 NAD + 2 NADH• Fermentation is an inefficient anaerobicredox process in which glucose becomesoxidized and an organic substancebecomes reduced• Some fungi and bacteria, as well asmuscle cells under conditions of lowoxygen, obtain low yields of <strong>ATP</strong> throughfermentation2 <strong>ATP</strong>CO 22 Pyruvate2 Ethyl alcohol(b) Alcohol fermentationFig. 8-13b, p. 187GlycolysisGlucose2 NAD + 2 NADHSummary Reaction• Complete oxidation of glucose2 <strong>ATP</strong>2 PyruvateC 6 H 12 O 6 + 6 O 2 + 6 H 2 O !6 CO 2 + 12 H 2 O + energy (36 to 38 <strong>ATP</strong>)2 Lactate(c) Lactate fermentationFig. 8-13c, p. 187Summary Reaction• GlycolysisC 6 H 12 O 6 + 2 <strong>ATP</strong> + 2 ADP + 2 P i + 2 NAD +! 2 pyruvate + 4 <strong>ATP</strong> + 2 NADH + H 2 O• Conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA2 pyruvate + 2 coenzyme A + 2 NAD + !2 acetyl CoA + 2 CO 2 + 2 NADHSummary Reaction• Citric acid cycle2 acetyl CoA + 6 NAD + + 2 FAD + 2 ADP+ 2 P i + 2 H 2 O ! 4 CO 2 + 6 NADH +2 FADH 2 + 2 <strong>ATP</strong> + 2 CoA• Hydrogen atoms in ETCNADH + 3 ADP + 3 P i + 12 O 2 ! NAD + + 3<strong>ATP</strong> + H 2 OFADH 2 + 2 ADP + 2 P i + 12 O 2 ! FAD + 2<strong>ATP</strong> + H 2 O