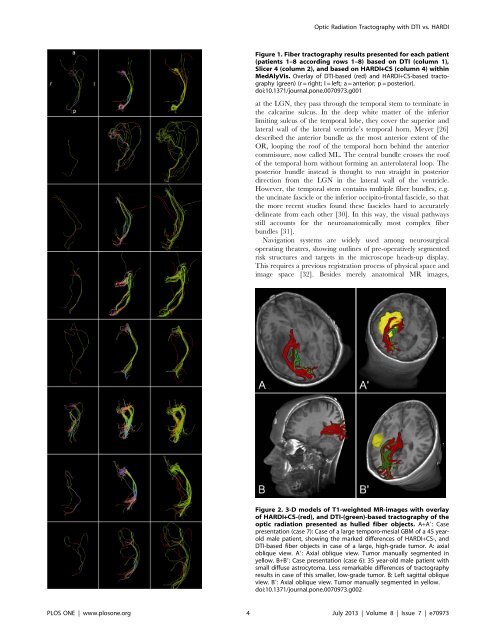
<strong>Optic</strong> <strong>Radiation</strong> <strong>Tractography</strong> with DTI vs. HARDIFigure 1. <strong>Fiber</strong> tractography results presented for each patient(patients 1–8 accord<strong>in</strong>g rows 1–8) based on DTI (column 1),<strong>Slicer</strong> 4 (column 2), and based on HARDI+CS (column 4) with<strong>in</strong>MedAlyVis. Overlay of DTI-based (red) and HARDI+CS-based tractography(green) (r = right; l = left; a = anterior; p = posterior).doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0070973.g001at the LGN, they pass through the temporal stem to term<strong>in</strong>ate <strong>in</strong>the calcar<strong>in</strong>e sulcus. In the deep white matter of the <strong>in</strong>feriorlimit<strong>in</strong>g sulcus of the temporal lobe, they cover the superior andlateral wall of the lateral ventricle’s temporal horn. Meyer [26]described the anterior bundle as the most anterior extent of theOR, loop<strong>in</strong>g the roof of the temporal horn beh<strong>in</strong>d the anteriorcommissure, now called ML. The central bundle crosses the roofof the temporal horn without form<strong>in</strong>g an anterolateral loop. Theposterior bundle <strong>in</strong>stead is thought to run straight <strong>in</strong> posteriordirection from the LGN <strong>in</strong> the lateral wall of the ventricle.However, the temporal stem conta<strong>in</strong>s multiple fiber bundles, e.g.the unc<strong>in</strong>ate fascicle or the <strong>in</strong>ferior occipito-frontal fascicle, so thatthe more recent studies found these fascicles hard to accuratelydel<strong>in</strong>eate from each other [30]. In this way, the visual pathwaysstill accounts for the neuroanatomically most complex fiberbundles [31].Navigation systems are widely used among neurosurgicaloperat<strong>in</strong>g theatres, show<strong>in</strong>g outl<strong>in</strong>es of pre-operatively segmentedrisk structures and targets <strong>in</strong> the microscope heads-up display.This requires a previous registration process of physical space andimage space [32]. Besides merely anatomical MR images,Figure 2. 3-D models of T1-weighted MR-images with overlayof HARDI+CS-(red), and DTI-(green)-based tractography of theoptic radiation presented as hulled fiber objects. A+A9: Casepresentation (case 7): Case of a large temporo-mesial GBM of a 45 yearoldmale patient, show<strong>in</strong>g the marked differences of HARDI+CS-, andDTI-based fiber objects <strong>in</strong> case of a large, high-grade tumor. A: axialoblique view. A9: Axial oblique view. Tumor manually segmented <strong>in</strong>yellow. B+B9: Case presentation (case 6): 35 year-old male patient withsmall diffuse astrocytoma. Less remarkable differences of tractographyresults <strong>in</strong> case of this smaller, low-grade tumor. B: Left sagittal obliqueview. B9: Axial oblique view. Tumor manually segmented <strong>in</strong> yellow.doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0070973.g002PLOS ONE | www.plosone.org 4 July 2013 | Volume 8 | Issue 7 | e70973
<strong>Optic</strong> <strong>Radiation</strong> <strong>Tractography</strong> with DTI vs. HARDIfunctional data have also been <strong>in</strong>tegrated <strong>in</strong> recent years, nowdesignated as multimodality navigation. This concept <strong>in</strong>cludes thedisplay of eloquent cortical sites (given for example by fMRI [33]),metabolic data (given for example by magnetic resonancespectroscopy imag<strong>in</strong>g [34], s<strong>in</strong>gle photon emission computedtomography) or major white matter tracts computed with fibertractography.The by far most frequently used basis for fiber tractography <strong>in</strong>the cl<strong>in</strong>ical practice is DTI, which is still developed further<strong>in</strong>clud<strong>in</strong>g the processes of data acquisition, image process<strong>in</strong>g andanalysis [35]. The pr<strong>in</strong>ciple DTI is based on the assumption thatdiffusion is faster alongside white matter tracts than perpendicularto the fiber bundle direction [6]. Although consist<strong>in</strong>g of one b0-image and at least six non-coll<strong>in</strong>ear diffusion images, today a totalof 30 gradient directions <strong>in</strong> a diffusion dataset has been proposedfor acceptable tractography results of neuroanatomically complexfiber bundles and is thus the basel<strong>in</strong>e standard for a DTI dataset[36]. One major restriction of the DTI technique is the<strong>in</strong>capability to resolve complex <strong>in</strong>tra-voxel diffusion profiles suchas cross<strong>in</strong>g, kiss<strong>in</strong>g or diverg<strong>in</strong>g fibers. However, this is of special<strong>in</strong>terest for tractography results of neuroanatomically complexfiber bundles like for example the visual pathways, particularly theOR <strong>in</strong> its course through the temporal lobe. So far, several groupshave already succeeded <strong>in</strong> a DTI-based reconstruction of ML andOR [27,37]. However their quantitative results (e.g. measureddistances from temporal lobe structures like the temporal horn orthe temporal pole) varied significantly [27,38,39]. A simiilarobservation was made <strong>in</strong> studies us<strong>in</strong>g pre-, and postoperativevisual field deficits for validation [37,39]. A major drawback is the<strong>in</strong>capability of DTI to resolve fibers <strong>in</strong> areas of disturbed diffusionreliably, which is most commonly the case <strong>in</strong> neurosurgical patientcollectives. Apart from DTI-tractography of the OR <strong>in</strong> temporallobe epilepsy [37], <strong>in</strong> which there is no structural change of thewhite matter, fiber tractography is of major <strong>in</strong>terest for temporalgliomas as highly <strong>in</strong>vasive and <strong>in</strong>filtrative tumors are hard todel<strong>in</strong>eate from the surround<strong>in</strong>g healthy bra<strong>in</strong> parenchyma.Although DTI-based tractography results have been shown tocontribute to a low postoperative morbidity when <strong>in</strong>tegrated <strong>in</strong> thenavigation system [4,5], comparable to electrostimulation methods[40,41], methods to provide even higher patient safety are stillunder <strong>in</strong>tense <strong>in</strong>vestigation:Apart from alternative approaches [42] or even the applicationof <strong>in</strong>traoperative DTI [43] us<strong>in</strong>g high-field <strong>in</strong>traoperative MRIsystems, several approaches for improvement of the DTItractographyprocedure itself have been published. Regard<strong>in</strong>gthe OR, there has to be mentioned fiber track<strong>in</strong>g from multipleseed volumes as proposed by Wu et al. [44] or Tao et al. [45],variations on the number of directional motion prob<strong>in</strong>g gradients[38] or tractography algorithms, for example the advanced fastmarch<strong>in</strong>g algorithm by Staempfli et al. [46] among others.Despite these <strong>in</strong>novations, the previously described <strong>in</strong>tr<strong>in</strong>sicdrawbacks of the 2 nd order tensor model rema<strong>in</strong>. These can beovercome by us<strong>in</strong>g advanced diffusion imag<strong>in</strong>g and reconstructionschemes based on HARDI. Us<strong>in</strong>g this approach, multiple<strong>in</strong>travoxel fiber orientations can be resolved. However, acquisitionof HARDI data sets requires a significantly higher number ofdiffusion gradients, rang<strong>in</strong>g from 60 to 100, with associated dataacquisition times of up to 25 m<strong>in</strong>utes as opposed to approximately4 m<strong>in</strong>utes for DTI (on 3T MRI-systems). In this way, cl<strong>in</strong>icalapplications of HARDI are still rare although frequently used fortheoretical neuroimag<strong>in</strong>g e.g. by Frey et al. [47].The disadvantage of <strong>in</strong>creased acquisition times has beenalleviated by HARDI+CS, which is based on the theory of sparserepresentation. Thus, CS enables the reconstruction of HARDIsignals from as low as 20 diffusion gradients, although with a lowreconstruction error of approximately 1%. In this way, ofconventional diffusion weighted data set, which is also used forDTI-based fiber tractography can be used for reconstruction [17].Apart from this, current research also addresses higherpracticability for HARDI-based fiber reconstruction <strong>in</strong> cl<strong>in</strong>icalapplications. Due to the <strong>in</strong>creased diffusion <strong>in</strong>formation providedby HARDI, naïve fiber track<strong>in</strong>g approaches based on HARDIdata are computationally expensive. Several frameworks havebeen proposed, for example by Prckowska et al. [48] us<strong>in</strong>g a fusedDTI/HARDI visualization or Reisert et al. [49].Particularly for reconstruction of neuroanatomically complexfiber bundles, a high impact of advanced diffusion models as basefor fiber tractography is likely. We <strong>in</strong>vestigated HARDI+CS’spossible advantages over DTI on the example of the OR <strong>in</strong> aneurosurgical patient collective, all patients suffer<strong>in</strong>g from gliomas<strong>in</strong> the temporal lobe with their associated more complex whitematter architecture.Interpretation of our tractography resultsThe basis for <strong>in</strong>terpretation of our results are classical and morerecently published dissection studies also mentioned above[27,28].In all eight cases, tractography results based on HARDI+CSdisplay the OR better compared with DTI-based fiber objects.HARDI+CS-based objects generally display more fibers, thusdisplay<strong>in</strong>g the OR as a solid tract <strong>in</strong>clud<strong>in</strong>g its three differentbundles. This suggests, accord<strong>in</strong>g to the recent literature that DTIbasedfiber tractography generally underdeterm<strong>in</strong>es the extent of afiber bundle [50].In six out of eight cases however, HARDI+CS-based fibertractography results <strong>in</strong> significantly improved fiber objects(patients 2–5, 7, 8) compared with DTI. In these cases, thes<strong>in</strong>gle-ROI DTI-based results only give slender fiber bundles(patients 3–5, 7) or even do not display the OR conv<strong>in</strong>c<strong>in</strong>gly at all(patients 2, 8).These obvious advantages of HARDI+CS-based fiber tractographyare particularly associated with the follow<strong>in</strong>g factors:– tumor size/size of peritumoral edema– tumor localization/distance from the OR– tumor histopathology– tumor morphology <strong>in</strong> MRIThus, <strong>in</strong> those cases for which HARDI+CS delivered significantlybetter results, we found a high-grade <strong>in</strong>vasive tumor <strong>in</strong> sixcases (patients 2–5, 7, 8), mostly associated with a significantperitumoral edema (4 cases: patients 2, 5, 7, 8). Only one of thesetumors (patient 3) did not show significant contrast enhancementon the T1-weighted MRI. Furthermore, the tumors were located<strong>in</strong> direct vic<strong>in</strong>ity to the OR based on HARDI+CS with less than15 mm <strong>in</strong> four cases (patients 4, 5, 7, 8). Compared to this, s<strong>in</strong>gle-ROI DTI-based fiber tractography resulted <strong>in</strong> acceptable objects<strong>in</strong> two patients (1 and 6). Here, both tumors showed no contrastenhancement <strong>in</strong> T1-weighted MRI, suggest<strong>in</strong>g less <strong>in</strong>vasivebehaviour, which was confirmed by histopathology (oligodendroglioma,diffuse astrocytoma). Furthermore, these tumors werecomparatively small accord<strong>in</strong>g to manual segmentation (35 cm 3and 16 cm 3 ).Compar<strong>in</strong>g our DTI-based tractography results of the OR withthose of other study groups, we can conclude that our results seemto be of lower quality. However, there are several explanations forthis: Most DTI-based tractography results were performed <strong>in</strong>healthy bra<strong>in</strong> [38,44,46,51] or, if used <strong>in</strong> neurosurgical practice, <strong>in</strong>PLOS ONE | www.plosone.org 5 July 2013 | Volume 8 | Issue 7 | e70973