View - Ecole Centrale Paris
View - Ecole Centrale Paris
View - Ecole Centrale Paris
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
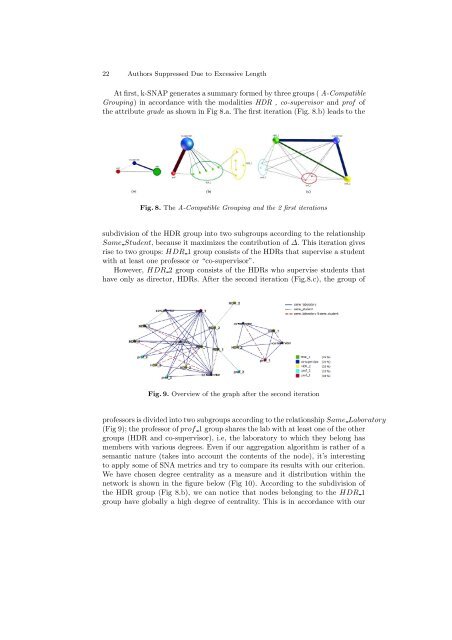
22 Authors Suppressed Due to Excessive LengthAtfirst,k-SNAPgeneratesasummaryformedbythreegroups(A-CompatibleGrouping) in accordance with the modalities HDR , co-supervisor and prof ofthe attribute grade as shown in Fig 8.a. The first iteration (Fig. 8.b) leads to theFig.8. The A-Compatible Grouping and the 2 first iterationssubdivision of the HDR group into two subgroups according to the relationshipSame Student, because it maximizes the contribution of ∆. This iteration givesrise to two groups: HDR 1 group consists of the HDRs that supervise a studentwith at least one professor or “co-supervisor”.However, HDR 2 group consists of the HDRs who supervise students thathave only as director, HDRs. After the second iteration (Fig.8.c), the group ofFig.9. Overview of the graph after the second iterationprofessorsisdividedintotwosubgroupsaccordingtotherelationshipSame Laboratory(Fig 9); the professor of prof 1 group shares the lab with at least one of the othergroups (HDR and co-supervisor), i.e, the laboratory to which they belong hasmembers with various degrees. Even if our aggregation algorithm is rather of asemantic nature (takes into account the contents of the node), it’s interestingto apply some of SNA metrics and try to compare its results with our criterion.We have chosen degree centrality as a measure and it distribution within thenetwork is shown in the figure below (Fig 10). According to the subdivision ofthe HDR group (Fig 8.b), we can notice that nodes belonging to the HDR 1group have globally a high degree of centrality. This is in accordance with our