Modeling and Optimization of Traffic Flow in Urban Areas - Czech ...
Modeling and Optimization of Traffic Flow in Urban Areas - Czech ...
Modeling and Optimization of Traffic Flow in Urban Areas - Czech ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
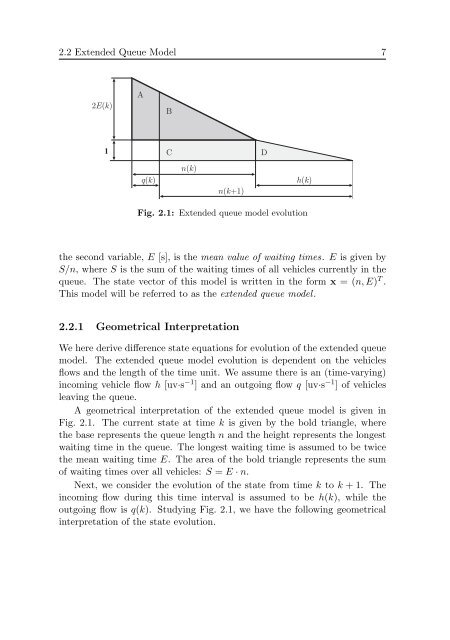
2.2 Extended Queue Model 72 E( k)AB1CDq( k)n( k)n( k+1)h( k)Fig. 2.1: Extended queue model evolutionthe second variable, E [s], is the mean value <strong>of</strong> wait<strong>in</strong>g times. E is given byS/n, where S is the sum <strong>of</strong> the wait<strong>in</strong>g times <strong>of</strong> all vehicles currently <strong>in</strong> thequeue. The state vector <strong>of</strong> this model is written <strong>in</strong> the form x = (n, E) T .This model will be referred to as the extended queue model.2.2.1 Geometrical InterpretationWe here derive difference state equations for evolution <strong>of</strong> the extended queuemodel. The extended queue model evolution is dependent on the vehiclesflows <strong>and</strong> the length <strong>of</strong> the time unit. We assume there is an (time-vary<strong>in</strong>g)<strong>in</strong>com<strong>in</strong>g vehicle flow h [uv·s −1 ] <strong>and</strong> an outgo<strong>in</strong>g flow q [uv·s −1 ] <strong>of</strong> vehiclesleav<strong>in</strong>g the queue.A geometrical <strong>in</strong>terpretation <strong>of</strong> the extended queue model is given <strong>in</strong>Fig. 2.1. The current state at time k is given by the bold triangle, wherethe base represents the queue length n <strong>and</strong> the height represents the longestwait<strong>in</strong>g time <strong>in</strong> the queue. The longest wait<strong>in</strong>g time is assumed to be twicethe mean wait<strong>in</strong>g time E. The area <strong>of</strong> the bold triangle represents the sum<strong>of</strong> wait<strong>in</strong>g times over all vehicles: S = E · n.Next, we consider the evolution <strong>of</strong> the state from time k to k + 1. The<strong>in</strong>com<strong>in</strong>g flow dur<strong>in</strong>g this time <strong>in</strong>terval is assumed to be h(k), while theoutgo<strong>in</strong>g flow is q(k). Study<strong>in</strong>g Fig. 2.1, we have the follow<strong>in</strong>g geometrical<strong>in</strong>terpretation <strong>of</strong> the state evolution.