Modeling and Optimization of Traffic Flow in Urban Areas - Czech ...
Modeling and Optimization of Traffic Flow in Urban Areas - Czech ...
Modeling and Optimization of Traffic Flow in Urban Areas - Czech ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
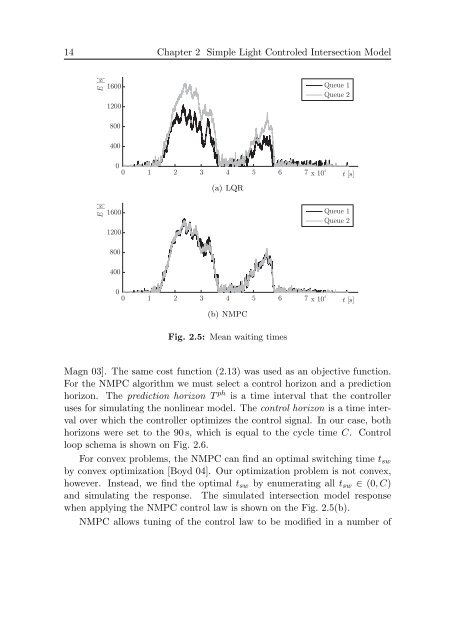
14 Chapter 2 Simple Light Controled Intersection ModelE [s]16001200Queue 1Queue 280040000 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 x 10 4(a) LQRt [s]E [s]16001200Queue 1Queue 280040000 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 x 10 4 t [s](b) NMPCFig. 2.5: Mean wait<strong>in</strong>g timesMagn 03]. The same cost function (2.13) was used as an objective function.For the NMPC algorithm we must select a control horizon <strong>and</strong> a predictionhorizon. The prediction horizon T ph is a time <strong>in</strong>terval that the controlleruses for simulat<strong>in</strong>g the nonl<strong>in</strong>ear model. The control horizon is a time <strong>in</strong>tervalover which the controller optimizes the control signal. In our case, bothhorizons were set to the 90 s, which is equal to the cycle time C. Controlloop schema is shown on Fig. 2.6.For convex problems, the NMPC can f<strong>in</strong>d an optimal switch<strong>in</strong>g time t swby convex optimization [Boyd 04]. Our optimization problem is not convex,however. Instead, we f<strong>in</strong>d the optimal t sw by enumerat<strong>in</strong>g all t sw ∈ (0, C)<strong>and</strong> simulat<strong>in</strong>g the response. The simulated <strong>in</strong>tersection model responsewhen apply<strong>in</strong>g the NMPC control law is shown on the Fig. 2.5(b).NMPC allows tun<strong>in</strong>g <strong>of</strong> the control law to be modified <strong>in</strong> a number <strong>of</strong>