Modeling and Optimization of Traffic Flow in Urban Areas - Czech ...
Modeling and Optimization of Traffic Flow in Urban Areas - Czech ...
Modeling and Optimization of Traffic Flow in Urban Areas - Czech ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
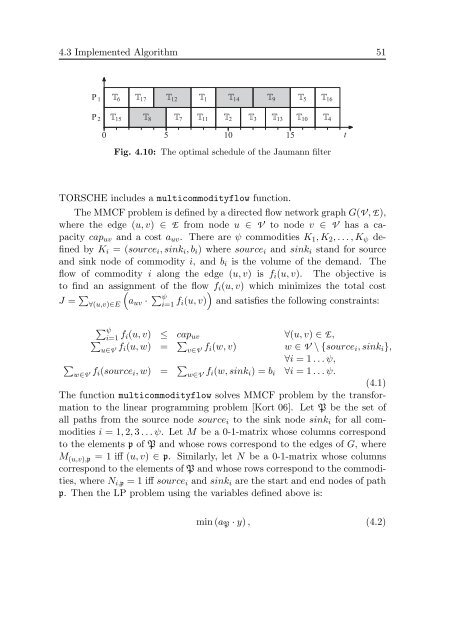
4.3 Implemented Algorithm 51P 2P 1 T 6 T 17 T 12 T 1 T 14 T 9 T 5 T 16T 15 T 8 T 7 T 11 T 2 T 3 T 13 T 10 T 40 5 10 15 tFig. 4.10: The optimal schedule <strong>of</strong> the Jaumann filterTORSCHE <strong>in</strong>cludes a multicommodityflow function.The MMCF problem is def<strong>in</strong>ed by a directed flow network graph G(V , E),where the edge (u, v) ∈ E from node u ∈ V to node v ∈ V has a capacitycap uv <strong>and</strong> a cost a uv . There are ψ commodities K 1 , K 2 , . . . , K ψ def<strong>in</strong>edby K i = (source i , s<strong>in</strong>k i , b i ) where source i <strong>and</strong> s<strong>in</strong>k i st<strong>and</strong> for source<strong>and</strong> s<strong>in</strong>k node <strong>of</strong> commodity i, <strong>and</strong> b i is the volume <strong>of</strong> the dem<strong>and</strong>. Theflow <strong>of</strong> commodity i along the edge (u, v) is f i (u, v). The objective isto f<strong>in</strong>d an assignment <strong>of</strong> the flow f i (u, v) which m<strong>in</strong>imizes the total costJ = ∑ (∀(u,v)∈Ea uv · ∑ψ )i=1 f i(u, v) <strong>and</strong> satisfies the follow<strong>in</strong>g constra<strong>in</strong>ts:∑ ψi=1 f i(u, v) ≤ cap uv ∀(u, v) ∈ E,∑u∈V f i(u, w) = ∑ v∈V f i(w, v) w ∈ V \ {source i , s<strong>in</strong>k i },∀i = 1 . . . ψ,∑w∈V f i(source i , w) = ∑ w∈V f i(w, s<strong>in</strong>k i ) = b i ∀i = 1 . . . ψ.(4.1)The function multicommodityflow solves MMCF problem by the transformationto the l<strong>in</strong>ear programm<strong>in</strong>g problem [Kort 06]. Let P be the set <strong>of</strong>all paths from the source node source i to the s<strong>in</strong>k node s<strong>in</strong>k i for all commoditiesi = 1, 2, 3 . . . ψ. Let M be a 0-1-matrix whose columns correspondto the elements p <strong>of</strong> P <strong>and</strong> whose rows correspond to the edges <strong>of</strong> G, whereM (u,v),p = 1 iff (u, v) ∈ p. Similarly, let N be a 0-1-matrix whose columnscorrespond to the elements <strong>of</strong> P <strong>and</strong> whose rows correspond to the commodities,where N i,p = 1 iff source i <strong>and</strong> s<strong>in</strong>k i are the start <strong>and</strong> end nodes <strong>of</strong> pathp. Then the LP problem us<strong>in</strong>g the variables def<strong>in</strong>ed above is:m<strong>in</strong> (a P · y) , (4.2)