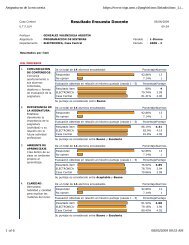
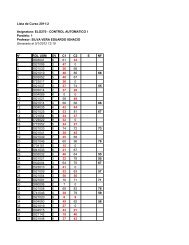
- Page 2 and 3: iiACKNOWLEDGMENTSI am truly gratefu
- Page 4 and 5: ivPage2.5.1 Traditional objective a
- Page 6 and 7: viPage6.3.1 Evaluation of uncoupled
- Page 8 and 9: viiiTablePage4.3 HSV measures taken
- Page 10 and 11: xFigurePage4.4 Downward pitch glide
- Page 12 and 13: xiiFigurePage5.12 Application of ai
- Page 14 and 15: xivFigurePage6.26 Uncoupled glottal
- Page 16 and 17: xviABBREVIATIONSAC Alternating curr
- Page 18 and 19: 11. INTRODUCTIONThis chapter introd
- Page 20 and 21: 3methods incorrectly suppress rippl
- Page 22 and 23: 5this hypothesis would validate cur
- Page 24 and 25: 72. BACKGROUNDThe increasing intere
- Page 26 and 27: 9flow in the vocal tract in time do
- Page 28 and 29: 112.1.2 The glottal impedanceThe gl
- Page 30 and 31: 13with previous considerations on t
- Page 32 and 33: 152.1.4 Self-oscillating models of
- Page 36 and 37: 19known as non-modal phonation. Non
- Page 38 and 39: 212.3 Bifurcations in voice product
- Page 40 and 41: 23Numerical models have also served
- Page 42 and 43: 25an all-pole system, this instabil
- Page 44 and 45: 27data points to obtain an acceptab
- Page 46 and 47: 29High-speed video is expected to s
- Page 48 and 49: 31recordings of normal vocal activi
- Page 50 and 51: 33ject’s radiated voice in the ro
- Page 52 and 53: 35simply increasing the body stiffn
- Page 54 and 55: 37quently proposed [74,97]. However
- Page 56 and 57: 39was used, where the index α indi
- Page 58 and 59: 41P kd = (P s + p s − p o )/(1
- Page 60 and 61: 43Table 3.1Material properties used
- Page 62 and 63: 451.5Glottis10.5Radius (cm)0Subglot
- Page 64 and 65: 471500Glottal airflowUoUg1500Glotta
- Page 66 and 67: 49a different origin. In all cases,
- Page 68 and 69: 51Data from recordings on human sub
- Page 70 and 71: 530.04Driving forces0.05Driving for
- Page 72 and 73: 55500400Intraglottal pressure distr
- Page 74 and 75: Table 3.5Simulations from body-cove
- Page 76 and 77: Table 3.7Simulations from body-cove
- Page 78 and 79: 61When contrasting incomplete closu
- Page 80 and 81: 63800700Glottal airflowUoUg50040030
- Page 82 and 83: 65Table 3.8Summary of selected glot
- Page 84 and 85:
671000900Glottal airflowUoUg500400G
- Page 86 and 87:
69Table 3.9Summary of selected glot
- Page 88 and 89:
713.3 DiscussionThe initial observa
- Page 90 and 91:
73chapter better represented the no
- Page 92 and 93:
754.1 MethodsThe vocal exercises an
- Page 94 and 95:
Fig. 4.1. High-speed video measurem
- Page 96 and 97:
79from the subject’s mouth (air-b
- Page 98 and 99:
81Instabilities occurring when F 0
- Page 100 and 101:
83Fig. 4.3. Endoscopic view obtaine
- Page 102 and 103:
85Table 4.1Pitch glides exhibiting
- Page 104 and 105:
87CV mask and endoscope on the unst
- Page 106 and 107:
89excursion was observed right befo
- Page 108 and 109:
91the 50 ms following the break. Th
- Page 110 and 111:
Fig. 4.9. Synchronous representatio
- Page 112 and 113:
95Table 4.3HSV measures taken from
- Page 114 and 115:
970Falsetto register0Chest register
- Page 116 and 117:
99To better describe the EOF weight
- Page 118 and 119:
101the acoustically-induced case wh
- Page 120 and 121:
103to evaluate the most adequate cl
- Page 122 and 123:
1055. BIOSENSING CONSIDERATIONS FOR
- Page 124 and 125:
107artificial compound (Akton of 1/
- Page 126 and 127:
Fig. 5.2. Bioacoustic Transducer Te
- Page 128 and 129:
111subjects were in the 20-30 age r
- Page 130 and 131:
1135.1.3 Relationship between sensi
- Page 132 and 133:
115Fig. 5.4. Tissue-borne and air-b
- Page 134 and 135:
Fig. 5.5. Effect on the air-borne s
- Page 136 and 137:
119Fig. 5.7. Changes in the respons
- Page 138 and 139:
Fig. 5.9. Effect of different surfa
- Page 140 and 141:
123favoring the tissue-borne path b
- Page 142 and 143:
1255.3.3 Translating the sensitivit
- Page 144 and 145:
1276. COUPLED AND UNCOUPLED IMPEDAN
- Page 146 and 147:
129Fig. 6.1. Representation of a di
- Page 148 and 149:
131(a) Vowel /a/(b) Vowel /i/Fig. 6
- Page 150 and 151:
133andZ rad = jωM accA acc. (6.10)
- Page 152 and 153:
135Fig. 6.6. Laser grid used for HS
- Page 154 and 155:
137experimentally [64] and thus wer
- Page 156 and 157:
139viscous losses, inertance, and c
- Page 158 and 159:
141schemes were noted, particularly
- Page 160 and 161:
143Airflow (cm 3 /s)400350300250200
- Page 162 and 163:
145Nevertheless, it was noted that
- Page 164 and 165:
147Airflow (cm 3 /s)350300250200150
- Page 166 and 167:
149(a) Vowel /a/ - fully open(b) Vo
- Page 168 and 169:
151for the chest register. These tr
- Page 170 and 171:
153750700Estimates from glottal air
- Page 172 and 173:
155It is noticeable from these comp
- Page 174 and 175:
157300250Estimates of glottal airfl
- Page 176 and 177:
159250200Estimates of glottal airfl
- Page 178 and 179:
161signal to derive useful quantiti
- Page 180 and 181:
163invariant impedance ( ˜Z g ), d
- Page 182 and 183:
165Uncoupled glottal volume velocit
- Page 184 and 185:
167500450400Linearized glottal impe
- Page 186 and 187:
169500450400Linearized glottal impe
- Page 188 and 189:
171The estimated uncoupled airflows
- Page 190 and 191:
173600500Uncoupled glottal volume v
- Page 192 and 193:
175600500Uncoupled glottal volume v
- Page 194 and 195:
177200Linearized glottal impedanceZ
- Page 196 and 197:
179Uncoupled glottal volume velocit
- Page 198 and 199:
1816.4 DiscussionNumerical simulati
- Page 200 and 201:
183less pronounced coupling (i.e.,
- Page 202 and 203:
1857. CONCLUSIONSThe principal aims
- Page 204 and 205:
187The biosensing experiments indic
- Page 206 and 207:
LIST OF REFERENCES
- Page 208 and 209:
190[13] K. N. Stevens, Acoustic pho
- Page 210 and 211:
192[42] B. H. Story and I. R. Titze
- Page 212 and 213:
194[74] I. R. Titze, “Regulating
- Page 214 and 215:
196[105] C. Tao and J. J. Jiang,
- Page 216 and 217:
198[135] J. Makhoul, “Linear pred
- Page 218 and 219:
200[166] J. Xu, J. Cheng, and Y. Wu
- Page 220 and 221:
202[194] J. G. Švec, F. Šram, and
- Page 222 and 223:
VITA