Grid Job Routing Algorithms - Phosphorus
Grid Job Routing Algorithms - Phosphorus
Grid Job Routing Algorithms - Phosphorus
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
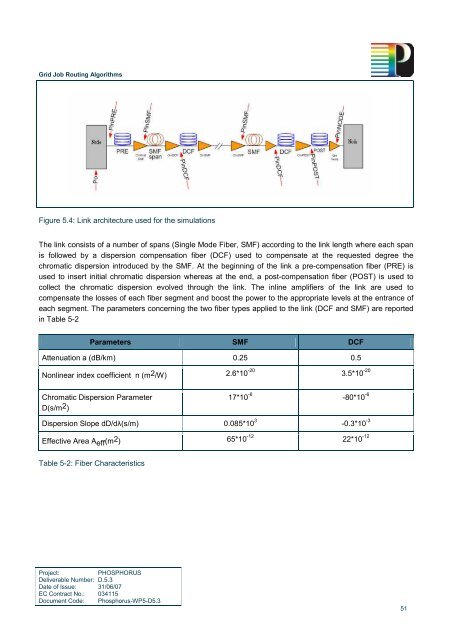
<strong>Grid</strong> <strong>Job</strong> <strong>Routing</strong> <strong>Algorithms</strong>Figure 5.4: Link architecture used for the simulationsThe link consists of a number of spans (Single Mode Fiber, SMF) according to the link length where each spanis followed by a dispersion compensation fiber (DCF) used to compensate at the requested degree thechromatic dispersion introduced by the SMF. At the beginning of the link a pre-compensation fiber (PRE) isused to insert initial chromatic dispersion whereas at the end, a post-compensation fiber (POST) is used tocollect the chromatic dispersion evolved through the link. The inline amplifiers of the link are used tocompensate the losses of each fiber segment and boost the power to the appropriate levels at the entrance ofeach segment. The parameters concerning the two fiber types applied to the link (DCF and SMF) are reportedin Table 5-2Parameters SMF DCFAttenuation a (dB/km) 0.25 0.5Nonlinear index coefficient n (m 2 /W) 2.6*10 -20 3.5*10 -20Chromatic Dispersion ParameterD(s/m 2 )17*10 -6 -80*10 -6Dispersion Slope dD/dλ(s/m) 0.085*10 3 -0.3*10 -3Effective Area A eff (m 2 ) 65*10 -12 22*10 -12Table 5-2: Fiber CharacteristicsProject:PHOSPHORUSDeliverable Number: D.5.3Date of Issue: 31/06/07EC Contract No.: 034115Document Code: <strong>Phosphorus</strong>-WP5-D5.351