Here - SAARC Human Resource Development Centre
Here - SAARC Human Resource Development Centre
Here - SAARC Human Resource Development Centre
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
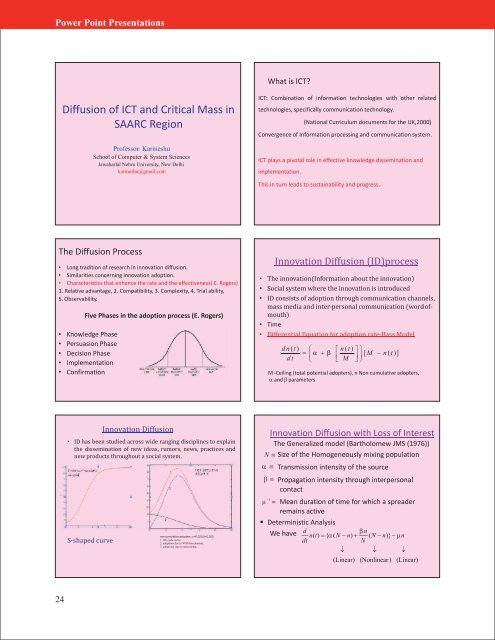
Power Point PresentationsWhat is ICT?Diffusion of ICT and Critical Mass in<strong>SAARC</strong> RegionProfessor KarmeshuSchool of Computer & System SciencesJawaharlal Nehru University, New Delhikarmeshu@gmail.comICT: Combination of information technologies with other relatedtechnologies, specifically communication technology.(National Curriculum documents for the UK,2000)Convergence of Information processing and communication system.ICT plays a pivotal role in effective knowledge dissemination andimplementation.This in turn leads to sustainability and progress.The Diffusion Process• Long tradition of research in innovation diffusion.• Similarities concerning innovation adoption.• Characteristics that enhance the rate and the effectiveness( E. Rogers)1. Relative advantage, 2. Compatibility, 3. Complexity, 4. Trial ability,5. Observability.Five Phases in the adoption process (E. Rogers)• Knowledge Phase• Persuasion Phase• Decision Phase• Implementation• ConfirmationInnovation Diffusion (ID)process• The innovation(Information about the innovation)• Social system where the innovation is introduced• ID consists of adoption through communication channels,mass media and inter-personal communication (word-ofmouth)• Time• Differential Equation for adoption rate-Bass Modeld n ( t ) n ( t ) [ M n ( t )]d t M M -Ceiling (total potential adopters), n Non cumulative adopters,and parametersInnovation Diffusion• ID has been studied across wide ranging disciplines to explainthe dissemination of new ideas, rumors, news, practices andnew products throughout a social system.S-shaped curvenon cumulative adopters .=0.020,ß=0.300.1. life cycle curve2. adoptions due to WOM mechanism,3. adoptions due to mass media.Innovation Diffusion with Loss of InterestThe Generalized model (Bartholomew JMS (1976))N Size of the Homogeneously mixing population Transmission intensity of the source Propagation intensity through interpersonalcontact1 Mean duration of time for which a spreaderremains activeDeterministic AnalysisWe have dnn( t) { ( N n) ( N n)}ndtN (Linear) (Nonlinear ) (Linear)24