IST-4-027756 WINNER II D6.13.12 v1.0 Final CG “local area ...
IST-4-027756 WINNER II D6.13.12 v1.0 Final CG “local area ...
IST-4-027756 WINNER II D6.13.12 v1.0 Final CG “local area ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
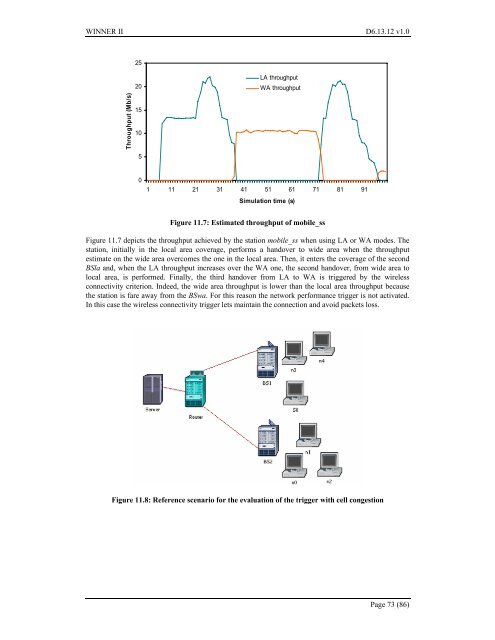
<strong>WINNER</strong> <strong>II</strong> <strong>D6.13.12</strong> <strong>v1.0</strong>25Throughput (Mb/s)2015105LA throughputWA throughput01 11 21 31 41 51 61 71 81 91Simulation time (s)Figure 11.7: Estimated throughput of mobile_ssFigure 11.7 depicts the throughput achieved by the station mobile_ss when using LA or WA modes. Thestation, initially in the local <strong>area</strong> coverage, performs a handover to wide <strong>area</strong> when the throughputestimate on the wide <strong>area</strong> overcomes the one in the local <strong>area</strong>. Then, it enters the coverage of the secondBSla and, when the LA throughput increases over the WA one, the second handover, from wide <strong>area</strong> tolocal <strong>area</strong>, is performed. <strong>Final</strong>ly, the third handover from LA to WA is triggered by the wirelessconnectivity criterion. Indeed, the wide <strong>area</strong> throughput is lower than the local <strong>area</strong> throughput becausethe station is fare away from the BSwa. For this reason the network performance trigger is not activated.In this case the wireless connectivity trigger lets maintain the connection and avoid packets loss.Figure 11.8: Reference scenario for the evaluation of the trigger with cell congestionPage 73 (86)