What is a wave? The one-dimensional wave equation
What is a wave? The one-dimensional wave equation
What is a wave? The one-dimensional wave equation
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
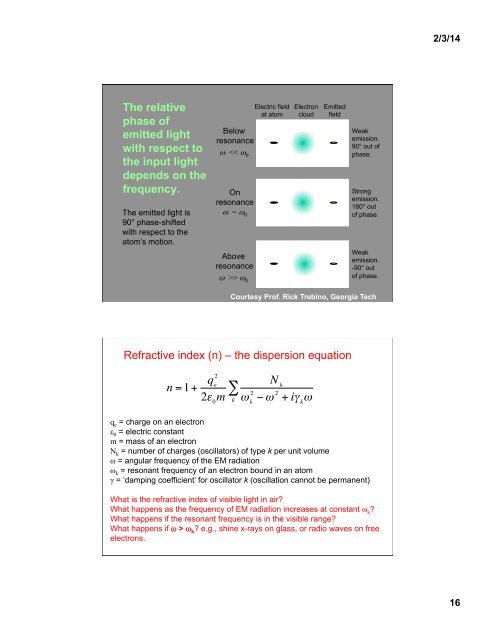
2/3/14<strong>The</strong> relativephase ofemitted lightwith respect tothe input lightdepends on thefrequency.<strong>The</strong> emitted light <strong>is</strong>90° phase-shiftedwith respect to theatom’s motion.Belowresonanceω > ω 0Electric fieldat atomElectroncloudEmittedfieldWeakem<strong>is</strong>sion.90° out ofphase.Strongem<strong>is</strong>sion.180° outof phase.Weakem<strong>is</strong>sion.-90° outof phase.Courtesy Prof. Rick Trebino, Georgia TechRefractive index (n) – the d<strong>is</strong>persion <strong>equation</strong>n = 1+q 2e2ε 0m∑kq e = charge on an electronε 0 = electric constantm = mass of an electronN k € = number of charges (oscillators) of type k per unit volumeω = angular frequency of the EM radiationω k = resonant frequency of an electron bound in an atomγ = ‘damping coefficient’ for oscillator k (oscillation cannot be permanent)<strong>What</strong> <strong>is</strong> the refractive index of v<strong>is</strong>ible light in air?<strong>What</strong> happens as the frequency of EM radiation increases at constant ω k ?<strong>What</strong> happens if the resonant frequency <strong>is</strong> in the v<strong>is</strong>ible range?<strong>What</strong> happens if ω > ω k ? e.g., shine x-rays on glass, or radio <strong>wave</strong>s on freeelectrons.N kω k2− ω 2 + iγ kω16