PE Pipe Technical Catalogue (PDF) - Pipelife Norge AS
PE Pipe Technical Catalogue (PDF) - Pipelife Norge AS
PE Pipe Technical Catalogue (PDF) - Pipelife Norge AS
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
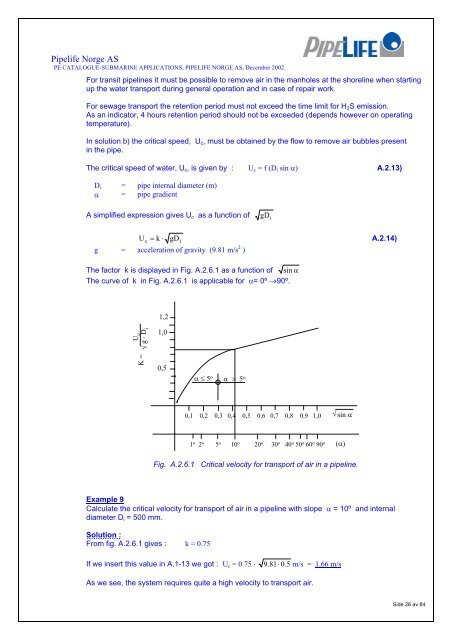
<strong>Pipe</strong>life <strong>Norge</strong> <strong>AS</strong><strong>PE</strong> CATALOGUE-SUBMARINE APPLICATIONS, PI<strong>PE</strong>LIFE NORGE <strong>AS</strong>, December 2002.For transit pipelines it must be possible to remove air in the manholes at the shoreline when startingup the water transport during general operation and in case of repair work.For sewage transport the retention period must not exceed the time limit for H 2 S emission.As an indicator, 4 hours retention period should not be exceeded (depends however on operatingtemperature).In solution b) the critical speed, U c , must be obtained by the flow to remove air bubbles presentin the pipe.The critical speed of water, U c , is given by : U c = f (D i sin α) A.2.13)D i = pipe internal diameter (m)α = pipe gradientA simplified expression gives U c as a function ofgD iU= k ⋅A.2.14)c gD ig = acceleration of gravity (9.81 m/s 2 )The factor k is displayed in Fig. A.2.6.1 as a function of sin αThe curve of k in Fig. A.2.6.1 is applicable for α= 0º →90º.1,2√ g ⋅ D iU c1,0K =0,5α ≤ 5 oα > 5 o0,1 0,2 0,3 0,4 0,5 0,6 0,7 0,8 0,9 1,0√ sin α1 o 2 o 5 o 10 o 20 o 30 o 40 o 50 o 60 o 90 o(α)Fig. A.2.6.1 Critical velocity for transport of air in a pipeline.Example 9Calculate the critical velocity for transport of air in a pipeline with slope α = 10º and internaldiameter D i = 500 mm.Solution :From fig. A.2.6.1 gives : k = 0.75If we insert this value in A.1-13 we got : U c = 0.75 ⋅ 9.81⋅ 0. 5 m/s = 1.66 m/sAs we see, the system requires quite a high velocity to transport air.Side 26 av 84