the same age group in rural areas. The main causes of death across all ages of the population over fiveyears old are stroke (15.4 percent), TB (7.5 percent), and injuries (6.5 percent). 4 According to theWorld <strong>Health</strong> Organization (WHO), ischaemic heart disease, lower respiratory infections, malaria,HIV/AIDS, and nutritional deficiencies also contribute to mortality rates (WHO, 2007).Many of Indonesia’s health indicators are improving; however, other indicators remain aconcern. Key health indicators, such as infant and child mortality, have improved steadily over the pastseveral decades. Despite these general trends, improvements in some indicators seem to have slowedin recent years. The infant mortality rate decreased from 36 deaths per 1,000 live births in 2002-03 to34 in 2007, while the under-five mortality rate decreased from 46 deaths per 1,000 live births to 44(Statistics Indonesia et al., 2008, henceforth referred to as the Indonesia Demographic and <strong>Health</strong>Survey [IDHS], 2008). Life expectancy at birth is 66 for men and 70 for women (World Bank, 2009c).Between 2002-03 and 2007, the fertility rate remained at 2.6 births per woman. Contraceptive useamong currently married women is high and has held steady at 61 percent (IDHS, 2008). Threeindicators remain a cause for concern: i) high child mortality; ii) high MMR; and iii) child malnutritionrates, which remain high at 25 percent for children under five and have largely stagnated since 2000(World Bank, 2008). Despite increases in the number of deliveries attended by a health professional(from 66 percent in 2002-03 to 79 percent in 2007) and the number of deliveries taking place in a healthfacility (40 percent to 46 percent) (IDHS, 2008), the MMR remains high. One study estimates MMR at420 deaths per 100,000 live births (Hill et al., 2007), while the IDHS estimates MMR at 228 deaths(IDHS, 2008). Irrespective of the wide discrepancy in these two estimates, Indonesia’s MMR is relativelyhigh compared to similar countries in the region.Comparing these indicators to the Millennium Development Goals (MDG), Indonesia appears on-trackto meet its child health targets. However, progress in maternal mortality is less clear (see Table 1).TABLE 1: STATUS OF PROGRESS TOWARD MDGS 5Indicator 1990 2007 Target (2015) StatusUnder-five mortality rate per 1,000 97 40 32 Likely to be achievedInfant mortality rate per 1,000 57 32 19 Likely to be achievedMaternal mortality rate per 100,000 390 307 110 Needs improvementSource: Target MDGs Project (a joint initiative of BAPPENAS and UNDP), December 2007.National health indicators mask significant disparities by region and socioeconomic status.Significant geographic disparities exist in health indicators such as life expectancy, infant and childmortality rates, and under-five malnutrition rates. For example, life expectancy in West Nusa Tenggarais 59 years compared with 72 years in Jogjakarta (World Bank, 2008). Infant mortality rates in WestSulawesi and West Nusa Tenggara are nearly three times greater than those in Jakarta and Central Java(IDHS, 2008). Significant variance in health indicators exists across socioeconomic quintiles. Despiteimproving overall trends in delivery care, most poor pregnant women deliver at home and 35 percent ofwomen in the lowest income quintile deliver without the benefit of a skilled birth attendant. Infant andchild mortality rates are more than four times higher among the poorest quintile (World Bank, 2006b).4 Results of the Basic <strong>Health</strong> Research were synthesized online in the article “Indonesia: Stroke and TB are Lead Killers,”published December 9, 2008, IR<strong>IN</strong> humanitarian news and analysis, UN Office for the Coordination of HumanitarianAffairs, available online at www.irinnews.org/Report.aspx?ReportId=81883.5 It should be noted that the National Statistics Bureau’s estimates for these indicators in 2007 included in this reportdiffer from the 2007 estimates published in the IDHS in 2008.4
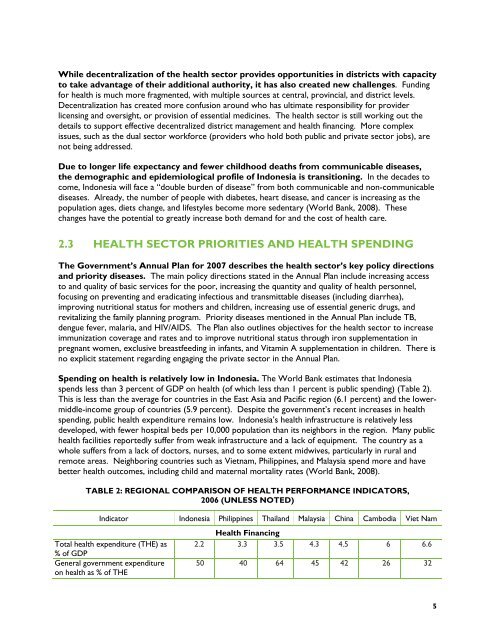
While decentralization of the health sector provides opportunities in districts with capacityto take advantage of their additional authority, it has also created new challenges. Fundingfor health is much more fragmented, with multiple sources at central, provincial, and district levels.Decentralization has created more confusion around who has ultimate responsibility for providerlicensing and oversight, or provision of essential medicines. The health sector is still working out thedetails to support effective decentralized district management and health financing. More complexissues, such as the dual sector workforce (providers who hold both public and private sector jobs), arenot being addressed.Due to longer life expectancy and fewer childhood deaths from communicable diseases,the demographic and epidemiological profile of Indonesia is transitioning. In the decades tocome, Indonesia will face a “double burden of disease” from both communicable and non-communicablediseases. Already, the number of people with diabetes, heart disease, and cancer is increasing as thepopulation ages, diets change, and lifestyles become more sedentary (World Bank, 2008). Thesechanges have the potential to greatly increase both demand for and the cost of health care.2.3 <strong>HEALTH</strong> <strong>SECTOR</strong> PRIORITIES AND <strong>HEALTH</strong> SPEND<strong>IN</strong>GThe Government’s Annual Plan for 2007 describes the health sector’s key policy directionsand priority diseases. The main policy directions stated in the Annual Plan include increasing accessto and quality of basic services for the poor, increasing the quantity and quality of health personnel,focusing on preventing and eradicating infectious and transmittable diseases (including diarrhea),improving nutritional status for mothers and children, increasing use of essential generic drugs, andrevitalizing the family planning program. Priority diseases mentioned in the Annual Plan include TB,dengue fever, malaria, and HIV/AIDS. The Plan also outlines objectives for the health sector to increaseimmunization coverage and rates and to improve nutritional status through iron supplementation inpregnant women, exclusive breastfeeding in infants, and Vitamin A supplementation in children. There isno explicit statement regarding engaging the private sector in the Annual Plan.Spending on health is relatively low in Indonesia. The World Bank estimates that Indonesiaspends less than 3 percent of GDP on health (of which less than 1 percent is public spending) (Table 2).This is less than the average for countries in the East Asia and Pacific region (6.1 percent) and the lowermiddle-incomegroup of countries (5.9 percent). Despite the government’s recent increases in healthspending, public health expenditure remains low. Indonesia’s health infrastructure is relatively lessdeveloped, with fewer hospital beds per 10,000 population than its neighbors in the region. Many publichealth facilities reportedly suffer from weak infrastructure and a lack of equipment. The country as awhole suffers from a lack of doctors, nurses, and to some extent midwives, particularly in rural andremote areas. Neighboring countries such as Vietnam, Philippines, and Malaysia spend more and havebetter health outcomes, including child and maternal mortality rates (World Bank, 2008).TABLE 2: REGIONAL COMPARISON OF <strong>HEALTH</strong> PERFORMANCE <strong>IN</strong>DICATORS,2006 (UNLESS NOTED)Indicator Indonesia Philippines Thailand Malaysia China Cambodia Viet NamTotal health expenditure (THE) as% of GDPGeneral government expenditureon health as % of THE<strong>Health</strong> Financing2.2 3.3 3.5 4.3 4.5 6 6.650 40 64 45 42 26 325
- Page 1: PRIVATE SECTOR HEALTHCARE IN INDONE
- Page 5: PRIVATE SECTOR HEALTH CAREIN INDONE
- Page 8 and 9: 7. Rationalizing Use of Medications
- Page 11 and 12: ABBREVIATIONSANCAskesAskeskinAusAID
- Page 13: THEUSAIDVATWHOTotal health expendit
- Page 17 and 18: EXECUTIVE SUMMARYAs documented in I
- Page 19 and 20: By using their power to select whic
- Page 21: higher reimbursement for complex de
- Page 25: 2. BACKGROUND2.1 GENERAL BACKGROUND
- Page 29: FIGURE 1: TOTAL EXPENDITURES ON HEA
- Page 32 and 33: poor, which only allows use of publ
- Page 34 and 35: Lack of overall investment in healt
- Page 36 and 37: • Pharmacists and drugsellers - A
- Page 38 and 39: 4.2 ASSESSMENT APPROACHData collect
- Page 40 and 41: practice, however, limited resource
- Page 42 and 43: Dinas to the hospital detailing the
- Page 44 and 45: Unlike Muhammadiyah and NU faciliti
- Page 46 and 47: TABLE 3: POPULATION COVERAGE BY HEA
- Page 48 and 49: customary fees. At the same time, i
- Page 51 and 52: 7. RATIONALIZING USE OFMEDICATIONS7
- Page 53 and 54: too few medicines to meet the publi
- Page 55 and 56: 8. PHARMACISTS ANDDRUGSELLERS AS PA
- Page 57 and 58: district provides TB drugs to priva
- Page 59 and 60: 9. ROLE OF PROFESSIONALASSOCIATIONS
- Page 61 and 62: IMA is involved in any allegations
- Page 63 and 64: 10. CONCLUSIONS ANDRECOMMENDATIONSI
- Page 65: If Indonesia is to achieve its prio
- Page 68 and 69: • Supporting the mapping of all f
- Page 71 and 72: ANNEX A: ASSESSMENT GUIDEIndonesia
- Page 73 and 74: Key Informants at Provincial LevelK
- Page 75: Key InformantsoooIBI, and memberrep
- Page 78 and 79:
Assessment Question Approach/Backgr
- Page 80 and 81:
Indicator Number Data Source and No
- Page 82 and 83:
1.3.4 DinKes Experience with Privat
- Page 84 and 85:
The team interviewed a manager 16 a
- Page 86 and 87:
They have used many different healt
- Page 88 and 89:
In Yogyakarta Province, there are 1
- Page 90 and 91:
graduates to work immediately in 24
- Page 92 and 93:
Muhammadiyah is a 226 bed hospital
- Page 94 and 95:
Dinas Yogyakarta31. Mardiningsih, S
- Page 96 and 97:
2.1 Provincial InformationThe popul
- Page 98 and 99:
How can services provided at privat
- Page 100 and 101:
The Provincial Health Office meets
- Page 102 and 103:
from multiple sources: 40 percent f
- Page 104 and 105:
2.9 Licensing and Oversight of Phar
- Page 106 and 107:
As per IMA Propinsi, they meet with
- Page 108 and 109:
It was mentioned that the budget fo
- Page 110 and 111:
• Private midwives are willing to
- Page 112 and 113:
etween PKBI and the District Health
- Page 114 and 115:
Cahya Kawaluyan Hospital has adapte
- Page 116 and 117:
the midwife to charge a slightly hi
- Page 118 and 119:
Involving Physicians in DOTS. A sig
- Page 120 and 121:
Ikatan Bidan Indonesia (IBI) West J
- Page 122 and 123:
Indicator DKI West Jakarta Data Sou
- Page 124 and 125:
visited an average of over 60 perce
- Page 126 and 127:
3.9 Potential role of professional
- Page 128 and 129:
members who pay membership fees. Th
- Page 130 and 131:
emainder paying out of pocket. Reve
- Page 132 and 133:
3.20 Indonesian Pharmacists Associa
- Page 134 and 135:
OtherApotek Gitamara, Jl. Kemanggis
- Page 136 and 137:
13. Government of Indonesia, World
- Page 138:
41. Thrabany, Hasbullah, et al. 200