Evaluation of the Tuberculosis Control Assistance Program (TB CAP)
Evaluation of the Tuberculosis Control Assistance Program (TB CAP)
Evaluation of the Tuberculosis Control Assistance Program (TB CAP)
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
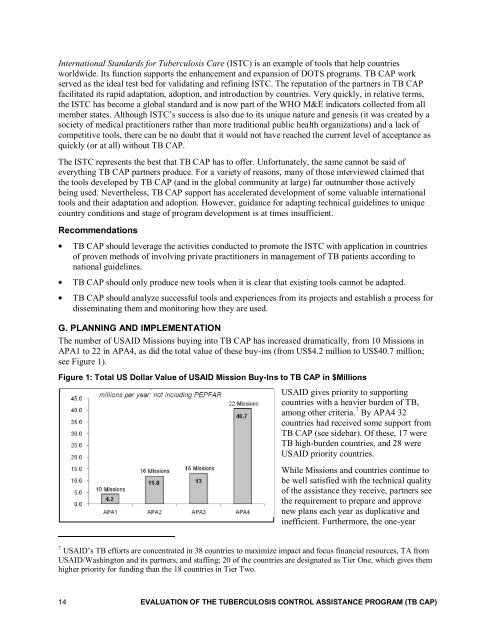
International Standards for <strong>Tuberculosis</strong> Care (ISTC) is an example <strong>of</strong> tools that help countriesworldwide. Its function supports <strong>the</strong> enhancement and expansion <strong>of</strong> DOTS programs. <strong>TB</strong> <strong>CAP</strong> workserved as <strong>the</strong> ideal test bed for validating and refining ISTC. The reputation <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> partners in <strong>TB</strong> <strong>CAP</strong>facilitated its rapid adaptation, adoption, and introduction by countries. Very quickly, in relative terms,<strong>the</strong> ISTC has become a global standard and is now part <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> WHO M&E indicators collected from allmember states. Although ISTC’s success is also due to its unique nature and genesis (it was created by asociety <strong>of</strong> medical practitioners ra<strong>the</strong>r than more traditional public health organizations) and a lack <strong>of</strong>competitive tools, <strong>the</strong>re can be no doubt that it would not have reached <strong>the</strong> current level <strong>of</strong> acceptance asquickly (or at all) without <strong>TB</strong> <strong>CAP</strong>.The ISTC represents <strong>the</strong> best that <strong>TB</strong> <strong>CAP</strong> has to <strong>of</strong>fer. Unfortunately, <strong>the</strong> same cannot be said <strong>of</strong>everything <strong>TB</strong> <strong>CAP</strong> partners produce. For a variety <strong>of</strong> reasons, many <strong>of</strong> those interviewed claimed that<strong>the</strong> tools developed by <strong>TB</strong> <strong>CAP</strong> (and in <strong>the</strong> global community at large) far outnumber those activelybeing used. Never<strong>the</strong>less, <strong>TB</strong> <strong>CAP</strong> support has accelerated development <strong>of</strong> some valuable internationaltools and <strong>the</strong>ir adaptation and adoption. However, guidance for adapting technical guidelines to uniquecountry conditions and stage <strong>of</strong> program development is at times insufficient.Recommendations<strong>TB</strong> <strong>CAP</strong> should leverage <strong>the</strong> activities conducted to promote <strong>the</strong> ISTC with application in countries<strong>of</strong> proven methods <strong>of</strong> involving private practitioners in management <strong>of</strong> <strong>TB</strong> patients according tonational guidelines.<strong>TB</strong> <strong>CAP</strong> should only produce new tools when it is clear that existing tools cannot be adapted.<strong>TB</strong> <strong>CAP</strong> should analyze successful tools and experiences from its projects and establish a process fordisseminating <strong>the</strong>m and monitoring how <strong>the</strong>y are used.G. PLANNING AND IMPLEMENTATIONThe number <strong>of</strong> USAID Missions buying into <strong>TB</strong> <strong>CAP</strong> has increased dramatically, from 10 Missions inAPA1 to 22 in APA4, as did <strong>the</strong> total value <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong>se buy-ins (from US$4.2 million to US$40.7 million;see Figure 1).Figure 1: Total US Dollar Value <strong>of</strong> USAID Mission Buy-Ins to <strong>TB</strong> <strong>CAP</strong> in $MillionsUSAID gives priority to supportingcountries with a heavier burden <strong>of</strong> <strong>TB</strong>,among o<strong>the</strong>r criteria. 7 By APA4 32countries had received some support from<strong>TB</strong> <strong>CAP</strong> (see sidebar). Of <strong>the</strong>se, 17 were<strong>TB</strong> high-burden countries, and 28 wereUSAID priority countries.While Missions and countries continue tobe well satisfied with <strong>the</strong> technical quality<strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> assistance <strong>the</strong>y receive, partners see<strong>the</strong> requirement to prepare and approvenew plans each year as duplicative andinefficient. Fur<strong>the</strong>rmore, <strong>the</strong> one-year7 USAID’s <strong>TB</strong> efforts are concentrated in 38 countries to maximize impact and focus financial resources, TA fromUSAID/Washington and its partners, and staffing; 20 <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> countries are designated as Tier One, which gives <strong>the</strong>mhigher priority for funding than <strong>the</strong> 18 countries in Tier Two.14 EVALUATION OF THE TUBERCULOSIS CONTROL ASSISTANCE PROGRAM (<strong>TB</strong> <strong>CAP</strong>)