veNTIlATIoN - Green Cross Publishing
veNTIlATIoN - Green Cross Publishing
veNTIlATIoN - Green Cross Publishing
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
probiotics<br />
38<br />
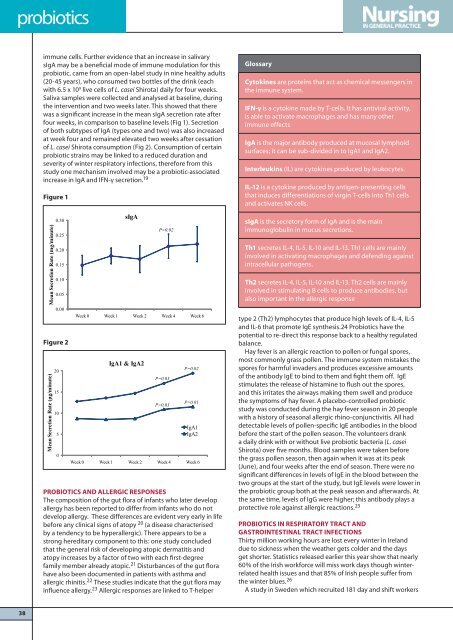
immune cells. Further evidence that an increase in salivary<br />
sIgA may be a beneficial mode of immune modulation for this<br />
probiotic, came from an open-label study in nine healthy adults<br />
(20-45 years), who consumed two bottles of the drink (each<br />
with 6.5 x 10 9 live cells of L. casei Shirota) daily for four weeks.<br />
Saliva samples were collected and analysed at baseline, during<br />
the intervention and two weeks later. This showed that there<br />
was a significant increase in the mean sIgA secretion rate after<br />
four weeks, in comparison to baseline levels (Fig 1). Secretion<br />
of both subtypes of IgA (types one and two) was also increased<br />
at week four and remained elevated two weeks after cessation<br />
of L. casei Shirota consumption (Fig 2). Consumption of certain<br />
probiotic strains may be linked to a reduced duration and<br />
severity of winter respiratory infections, therefore from this<br />
study one mechanism involved may be a probiotic-associated<br />
increase in IgA and IFN-γ secretion. 19<br />
Figure 1<br />
Mean Secretion Rate (mg/minute)<br />
Mean Secretion Rate (µg/minute)<br />
0.30<br />
0.25<br />
0.20<br />
0.15<br />
0.10<br />
0.05<br />
0.00<br />
Figure 2<br />
20<br />
15<br />
10<br />
5<br />
0<br />
sIgA<br />
IgA1 & IgA2<br />
P=0.02<br />
Week 0 Week 1 Week 2 Week 4 Week 6<br />
P=0.03<br />
P=0.03<br />
P=0.02<br />
P=0.01<br />
IgA1<br />
IgA2<br />
Week 0 Week 1 Week 2 Week 4 Week 6<br />
ProbIoTIcs ANd AllergIc resPoNses<br />
The composition of the gut flora of infants who later develop<br />
allergy has been reported to differ from infants who do not<br />
develop allergy. These differences are evident very early in life<br />
before any clinical signs of atopy 20 (a disease characterised<br />
by a tendency to be hyperallergic). There appears to be a<br />
strong hereditary component to this: one study concluded<br />
that the general risk of developing atopic dermatitis and<br />
atopy increases by a factor of two with each first-degree<br />
family member already atopic. 21 Disturbances of the gut flora<br />
have also been documented in patients with asthma and<br />
allergic rhinitis. 22 These studies indicate that the gut flora may<br />
influence allergy. 23 Allergic responses are linked to T-helper<br />
glossary<br />
cytokines are proteins that act as chemical messengers in<br />
the immune system.<br />
IFN-γ is a cytokine made by T-cells. It has antiviral activity,<br />
is able to activate macrophages and has many other<br />
immune effects<br />
IgA is the major antibody produced at mucosal lymphoid<br />
surfaces; it can be sub-divided in to IgA1 and IgA2.<br />
Interleukins (IL) are cytokines produced by leukocytes.<br />
Il-12 is a cytokine produced by antigen-presenting cells<br />
that induces differentiations of virgin T-cells into Th1 cells<br />
and activates NK cells.<br />
sIgA is the secretory form of IgA and is the main<br />
immunoglobulin in mucus secretions.<br />
Th1 secretes IL-4, IL-5, IL-10 and IL-13. Th1 cells are mainly<br />
involved in activating macrophages and defending against<br />
intracellular pathogens.<br />
Th2 secretes IL-4, IL-5, IL-10 and IL-13. Th2 cells are mainly<br />
involved in stimulating B cells to produce antibodies, but<br />
also important in the allergic response<br />
type 2 (Th2) lymphocytes that produce high levels of IL-4, IL-5<br />
and IL-6 that promote IgE synthesis.24 Probiotics have the<br />
potential to re-direct this response back to a healthy regulated<br />
balance.<br />
Hay fever is an allergic reaction to pollen or fungal spores,<br />
most commonly grass pollen. The immune system mistakes the<br />
spores for harmful invaders and produces excessive amounts<br />
of the antibody IgE to bind to them and fight them off. IgE<br />
stimulates the release of histamine to flush out the spores,<br />
and this irritates the airways making them swell and produce<br />
the symptoms of hay fever. A placebo-controlled probiotic<br />
study was conducted during the hay fever season in 20 people<br />
with a history of seasonal allergic rhino-conjunctivitis. All had<br />
detectable levels of pollen-specific IgE antibodies in the blood<br />
before the start of the pollen season. The volunteers drank<br />
a daily drink with or without live probiotic bacteria (L. casei<br />
Shirota) over five months. Blood samples were taken before<br />
the grass pollen season, then again when it was at its peak<br />
(June), and four weeks after the end of season. There were no<br />
significant differences in levels of IgE in the blood between the<br />
two groups at the start of the study, but IgE levels were lower in<br />
the probiotic group both at the peak season and afterwards. At<br />
the same time, levels of IgG were higher; this antibody plays a<br />
protective role against allergic reactions. 25<br />
ProbIoTIcs IN resPIrATory TrAcT ANd<br />
gAsTroINTesTINAl TrAcT INFecTIoNs<br />
Thirty million working hours are lost every winter in Ireland<br />
due to sickness when the weather gets colder and the days<br />
get shorter. Statistics released earlier this year show that nearly<br />
60% of the Irish workforce will miss work days though winterrelated<br />
health issues and that 85% of Irish people suffer from<br />
the winter blues. 26<br />
A study in Sweden which recruited 181 day and shift workers