Hammer and gouge mastoidectomy for acute mastoiditis - Vula ...
Hammer and gouge mastoidectomy for acute mastoiditis - Vula ...
Hammer and gouge mastoidectomy for acute mastoiditis - Vula ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
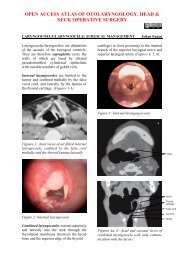
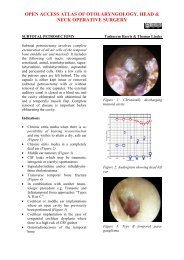
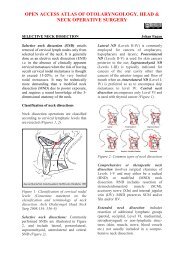
appearance of an egg. The spine of Henléremains <strong>and</strong> is the only really importantl<strong>and</strong>mark.Colour: Normally the bone appears whiteor oozes blood through the porous portionsof the retromeatal region. However, in<strong>mastoiditis</strong> the external cortex bleedsdiffusely due to the deep inflammatoryprocess. If there is underlying empyema,the wall appears bluish.4 th cut: 1cm behind 1 st , thus completinga circle of trephinationThe 1 st 3 taps of the <strong>gouge</strong> areperpendicular to the bony surfaceThe 4 th tap is applied obliquely toavoid the lateral sinus which may besuperficial or prominent.Surface: Some irregularities may appearalong the surface of the mastoid. Theseoften consist of inflammatory granulationswhich are apparent through the externalposterior petrosquamous suture or of afistula, which may be verified with the aidof a probe. The existence of a fistula issought wherever the incision hasuncovered free pus.Fourth Step: Trephining - Exploration ofSuperficial Antral RegionA large <strong>gouge</strong> is placed immediately belowthe linea temporalis (Figure 8). It is heldbetween the thumb <strong>and</strong> first two fingers,with the ring finger serving as a brake. Theinstrument is held in the position shown inthe illustration, being directed vertically atright angles to the bone surface.Site of Trephination: If a fistula is present<strong>and</strong> is at the level of the antral region or itsimmediate vicinity, the trephine isper<strong>for</strong>med at that level. If no fistula existsor is very far from the antral region, thetrephining is done as follows. An area ofapproach is outlined with the <strong>gouge</strong> byapplying it above <strong>and</strong> behind the canal atthe following points (Figures 9, 10):Figure 8: Trephining <strong>and</strong> exploring antralregionFifth Step: Exploration of SuperficialSubantral Region <strong>and</strong> TipAfter trephining <strong>and</strong> curetting thesuperficial antral region, the <strong>gouge</strong> isdirected toward the inferior portion of themastoid, making a superficial verticaltrench. The instrument is held between thethumb <strong>and</strong> first two fingers of the left h<strong>and</strong>with the two remaining fingers resting onthe bony surface to provide control <strong>and</strong> toavoid dangerous slip of the <strong>gouge</strong>.1 st cut: 2 - 3mm. behind spine of Henlé2 nd cut: just below linea temporalis3 rd cut: parallels, but 1cm. below 2 ndcut5