- Page 1 and 2: ABSTRACTEUSEBIO BALCAZAR, PAMELA EL
- Page 3 and 4: Effect of Breeder Nutrition and Fee
- Page 5 and 6: BIBLIOGRAPHYPamela Eliana Eusebio B
- Page 7 and 8: TABLE OF CONTENTSLIST OF TABLES …
- Page 9 and 10: Broiler Experiment 2 ..............
- Page 11 and 12: LIST OF TABLESCHAPTER ITable I-1. N
- Page 13 and 14: experiment 2 …………………
- Page 15 and 16: eeder feeder space change for the p
- Page 17 and 18: INTRODUCTIONThere is a worldwide co
- Page 19 and 20: importance according to reports fro
- Page 21 and 22: (Berry et al., 1996), ascorbic acid
- Page 23 and 24: Rotated TibiaRotated tibia is descr
- Page 25 and 26: Yolk and its lipid content also aff
- Page 27 and 28: Australia, Canada (Bird, 1997; Inte
- Page 29 and 30: except for copper that is mostly pr
- Page 31 and 32: Table I-3. Total phosphorus, phytat
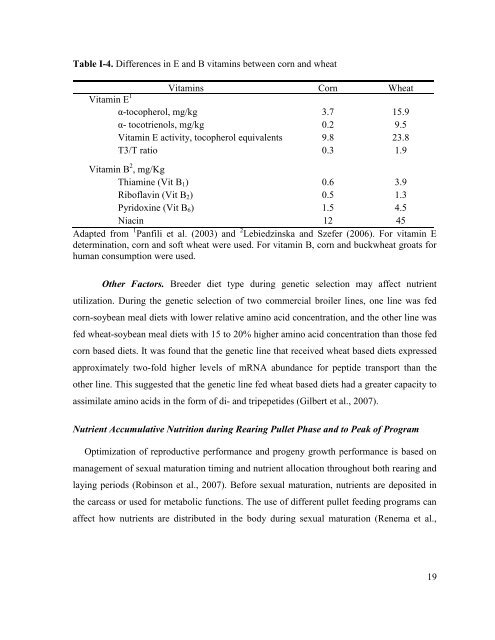
- Page 33: vitamin E, and the water-soluble an
- Page 37 and 38: REFERENCESAbdel-Salam, Z. A., A. M.
- Page 39 and 40: Choct, M. 1997. Feed Non-Starch Pol
- Page 41 and 42: Febrer, K., T. A. Jones, C. A. Donn
- Page 43 and 44: Johansson, K., J. Örberg, A. B. Ca
- Page 45 and 46: Leksrisompong, N., M. Argüelles-Ra
- Page 47 and 48: Nelson, T. S. 1967. The utilization
- Page 49 and 50: Reddi, A. H. 2000. Initiation and p
- Page 51 and 52: Starcher, B. C., C. H. Hill, and J.
- Page 53 and 54: Weiss, R. E., and A. H. Reddi. 1980
- Page 55 and 56: INTRODUCTIONThe nutrition and feedi
- Page 57 and 58: second objective was to determine t
- Page 59 and 60: feathers. Fertility was calculated
- Page 61 and 62: Table II-1. Composition of broiler
- Page 63 and 64: heavier (P < 0.05) compared with th
- Page 65 and 66: ABCFigure II-2. Effects of diet typ
- Page 67 and 68: Cumulative mortality (%)LevelsMain
- Page 69 and 70: Table II-3. Effects of diet type, f
- Page 71 and 72: Figure II-7. Effects of diet type (
- Page 73 and 74: Table II-4. P-values for the effect
- Page 75 and 76: Table II-6. P-values for the effect
- Page 77 and 78: DISCUSSIONBody Weights and Cumulati
- Page 79 and 80: Reproductive PerformanceReproductiv
- Page 81 and 82: Y:A ratio due to higher yolk percen
- Page 83 and 84: REFERENCESAltuntaş, E., and A. Şe
- Page 85 and 86:
Jong, I. C., V. S. Voorst, D. A. Eh
- Page 87 and 88:
Peebles E. D., C. D. Zumwalt, S. M.
- Page 89 and 90:
concluded that maternal diet type a
- Page 91 and 92:
The feeding program of female broil
- Page 93 and 94:
Hatching ExperimentAll the egg prod
- Page 95 and 96:
ijk : Effect of the second order in
- Page 97 and 98:
program, and the same feeder space
- Page 99 and 100:
Table III-2. Effect of breeder diet
- Page 101 and 102:
Table III-4. Effect of breeder/broi
- Page 103 and 104:
DISCUSSIONEgg Weight, Eggshell Prop
- Page 105 and 106:
eproductive tract. Melnychuk et al.
- Page 107 and 108:
CONCLUSIONSIt was concluded that br
- Page 109 and 110:
Cruickshank, E. M. 1934. Studies in
- Page 111 and 112:
Oviedo-Rondón, E. O., J. Small, M.
- Page 113 and 114:
Van der Eerden, B. C. J., M. Karper
- Page 115 and 116:
INTRODUCTIONBone development starts
- Page 117 and 118:
MATERIAL AND METHODSBroiler Breeder
- Page 119 and 120:
Chickens were group weighed at plac
- Page 121 and 122:
Pens were included as random effect
- Page 123 and 124:
Table IV-2. Composition of broiler
- Page 125 and 126:
corn-based diets produced progeny t
- Page 127 and 128:
Feed Conversion Ratio Adjusted for
- Page 129 and 130:
Table IV-4. Effects of diet type, m
- Page 131 and 132:
Maternal feeding programs alone aff
- Page 133 and 134:
Table IV-7. Effects of diet type, m
- Page 135 and 136:
Progeny Mortality. No significant (
- Page 137 and 138:
Six-wk-old male chickens from 32 an
- Page 139 and 140:
Table IV-11. Effects of diet type,
- Page 141 and 142:
Probability of observing crooked to
- Page 143 and 144:
At both breeder ages evaluated, pro
- Page 145 and 146:
progeny with more locomotion proble
- Page 147 and 148:
Hocking, P. M., and R. Bernard. 199
- Page 149 and 150:
CHAPTER V: EFFECT OF BREEDER FEEDIN
- Page 151 and 152:
Several previous investigations hav
- Page 153 and 154:
starter diet was fed from 0 to 4 wk
- Page 155 and 156:
At 46 wk, all eggs produced during
- Page 157 and 158:
Leg Health EvaluationAt 4 and 6 wk
- Page 159 and 160:
correct for variable number of broi
- Page 161 and 162:
RESULTSEgg CharacteristicsAt 31 wk,
- Page 163 and 164:
were smaller (P < 0.05) than chicke
- Page 165 and 166:
progeny compared to A strain broile
- Page 167 and 168:
Bone Traits and Bone Mineral Densit
- Page 169 and 170:
49-d body weight (g) of the progeny
- Page 171 and 172:
Probability of observing progenycro
- Page 173 and 174:
Probability of observing progenywal
- Page 175 and 176:
Progeny bone mineral density (g/cm
- Page 177 and 178:
Progeny bone mineral content (g)Pro
- Page 179 and 180:
eared under the same conditions dur
- Page 181 and 182:
Brake et al., 1997). Therefore, the
- Page 183 and 184:
that discard physical egg effects o
- Page 185 and 186:
practices and environmental conditi
- Page 187 and 188:
compared to the provision of less f
- Page 189 and 190:
Broilers that had greater prevalenc
- Page 191 and 192:
Brake, J., T. J. Walsh, and S. V. V
- Page 193 and 194:
Hayes, S. H., G. L. Cromwell, T. S.
- Page 195 and 196:
Meuer, H. J., and R. Baumann. 1988.
- Page 197 and 198:
Roberts, J. R., and M. Choct. 2006.
- Page 199 and 200:
Watkins, B. A. 1991. Importance of
- Page 201 and 202:
eeders restricted to the LS feeding